Summarize this article:
 951 Learners
951 LearnersLast updated on December 17, 2025
Factors of 32

Factors of 32 are whole numbers that can divide 32 completely. In real life, we use factors for grouping and sharing anything equally in the groups. In this article, we will be studying examples, mistakes, and methods to solve factors of 32.

What are the factors of 32
The factors of 32 can neither be a decimal nor a fraction. These factors divide 32 by, leaving zero as the remainder.
The factors of 32 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32.
- Negative Factors
These are negative counterparts of the positive factors
Negative factors: -1, -2, -4, -8, -16, -3.
- Prime Factors
Prime factors are the prime numbers themselves, when multiplied together, give 32 as the product.
Prime factor: 2
- Prime Factorization
Prime factorization involves breaking 32 into its prime factors
It is expressed as 25
The factors of 32 can be written as shown in the table given below:
| Factor Type | Values |
| Positive Factors of 32 | 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32 |
| Negative Factors of 32 | -1, -2, -4, -8, -16, -32 |
| Prime Factors of 32 | 2 |
| Prime Factorization of 32 | 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 2⁵ |
| The sum of the Factors of 32 | 63 |

How to Find the Factors of 32?
There are different methods to find the factors of 32.
Methods to find the factors of 32:
- Multiplication Method
- Division Method
- Prime Factor and Prime Factorization

Finding Factors Using Multiplication Method
The multiplication method finds the pair of factors that give 32 as their product.
Step-by-step process
Step 1: Find the pair of numbers whose product is 32.
Step 2: The factors are those numbers, when multiplied, give 32.
Step 3: Make a list of numbers whose product will be 32.
A list of numbers whose products are 32 is given below:
1 × 32 = 32
2 × 16 = 32
4 × 8 = 32

Explore Our Programs



Finding Factors Using Division Method
The division method finds the numbers that fully divide the given number.
Step-by-step process
Step 1: Since every number is divisible by 1, 1 will always be a factor. Example: 32÷1 = 32
%20(1).png?updatedAt=1727359870611)
Step 2: Move to the next integer. Both divisor and quotient are the factors. Example: 32÷2 = 16 and so on.
.png?updatedAt=1727359870992)
Picture showing the division method:
%20(1).png?updatedAt=1727359870594)

Prime Factors and Prime Factorization
- Multiplying prime numbers to get the given number as their product is called prime factors.
- Prime factorization is breaking down the number into its prime factors.

Prime Factors of 32
Number 32 has only one prime factor.
Prime factor of 32: 2
To find the prime factors of 32, divide 32 with the prime number 2
- 32÷2 = 16
- 16÷2 = 8
- 8÷2 = 4
- 4÷2 =2
- 2÷2 =1

Prime Factorization of 32
Prime Factorization breaks down the prime factors of 32
Expressed as 25
Factor Tree
The prime factorization is visually represented using the factor tree. It helps to understand the process easily. In this factor tree, each branch splits into prime factors.
Factor Tree for 32:
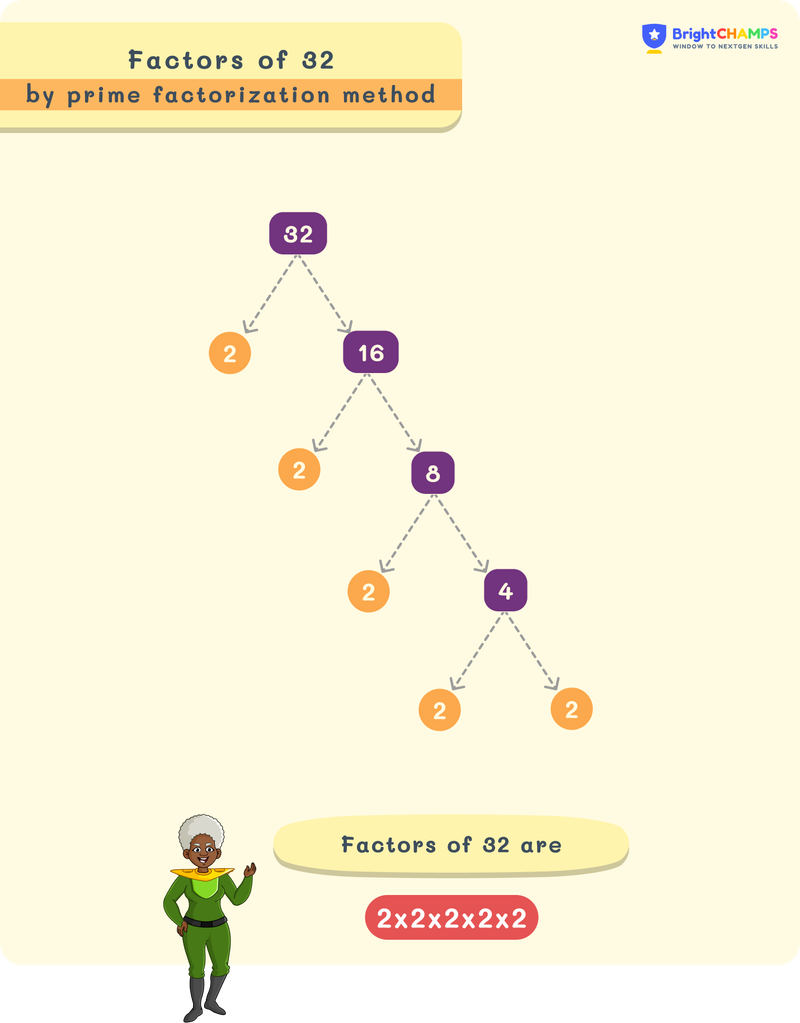

Factor Pairs of 32
The factors of 32 can be written in both positive and negative pairs. The table below represents the factor pairs of 32, where the product of each pair of numbers is equal to 32.
Positive Pair Factors of 32:
| Factors | Positive Pair Factors |
| 1 × 32 = 32 | 1, 32 |
| 2 × 16 = 32 | 2, 16 |
| 4 × 8 = 32 | 4, 8 |
Since the product of two negative numbers is also positive, 32 also has negative pair factors.
Negative Pair Factors of 32:
| Factors | Negative Pair Factors |
| −1 × −32 = 32 | −1, −32 |
| −2 × −16 = 32 | −2, −16 |
| −4 × −8 = 32 | −4, −8 |

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them in Factors of 32
Mistakes can occur while finding the factors. Learn about the common errors that can occur. Solutions to solve the common mistakes are given below.

Examples on Factors of 32

Problem 1
Can you identify the factor pair with one prime and one composite number?

Yes, the factor pair with one prime and composite number is (2,16)
Explanation
When (2,16) is multiplied we get 32 as the product. The number 2 is prime and 16 is composite.

Problem 2
What is the GCF of 32 and 16?

Factors of 32: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32
Factors of 16: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16
The GCF of 32 and 16 is 16.
Explanation
To find the GCF, list the factors of 32 and 16. From the factor list, you identify the greatest common factor.

Problem 3
Is 32 a factor of 32?

Yes, 32 is a factor of 32.
Explanation
Every number is a factor of itself because it is completely divisible by 1.

Problem 4
In New York City, a teacher buys 32 juice boxes from Walmart to distribute equally among students during a school science activity. She wants to divide them so that each group gets the same number of juice boxes with none left over. What are the possible group sizes she can form using all 32 juice boxes?

1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32
Explanation
To find the possible group sizes, we list all the factors of 32.
Factors are numbers that divide 32 evenly without leaving a remainder. The factors of 32 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32. Each of these represents a valid group size.

Problem 5
During an NFL fan meet-up in Dallas, organizers have 32 VIP wristbands to give away. Each fan group must receive the same number of wristbands, and no wristband can be left unused. What are all the possible numbers of fans that can be in each group?

1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32
Explanation
This is a factors problem because the wristbands must be divided evenly.
Any number that divides 32 exactly is a valid group size. Listing all such numbers gives the factors of 32: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32.

Problem 6
A pharmacy in Chicago fills a prescription at CVS using 32 tablets for a patient. The doctor instructs that the tablets must be taken in equal doses per day, with no tablets left over. What are the possible numbers of tablets the patient can take each day?

1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32
Explanation
Since the tablets must be divided evenly across days, we look for numbers that divide 32 exactly.
These numbers are called factors. The factors of 32 are 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32, which represent all possible daily dosage options.


FAQs on Factors of 32
1.What is the most common factor of 32?
2.Is 32 a factor of 16?
3.Is 32 prime or composite?
4.What can divide 32 and 56?
5.What are the multiples of 32?
6.How many factors does 32 have?
7.What is the smallest factor of 32?
8.What is the largest factor of 32?
9.Which factors of 32 add up to 13?
10.How many even factors does 32 have?
11.What are the odd factors of 32?
12.What is the sum of all the factors of 32?


Hiralee Lalitkumar Makwana
About the Author
Hiralee Lalitkumar Makwana has almost two years of teaching experience. She is a number ninja as she loves numbers. Her interest in numbers can be seen in the way she cracks math puzzles and hidden patterns.
Fun Fact
: She loves to read number jokes and games.




























