Summarize this article:
 1059 Learners
1059 LearnersLast updated on December 11, 2025
Factors of 49

Numbers whose dividend is completely divisible by quotient are its factors. The factor of 49 can neither be a decimal nor a fraction.

What are the Factors of 49
1,7 and 49 are the factors of 49.
Negative Factors of 49
These are the negative counterparts of positive factors. The negative factors are -1, -7, -49
Prime Factors of 49
Prime factors are the prime numbers when multiplied, give 49 and 7 is the only prime factor of 49.
Prime Factorization of 49
Process of breaking the given number into its prime factors. Prime Factorization: 72
An overview of the factors of 49
|
Positive Factors |
1, 7, 49 |
|
Negative Factors |
-1, -7, -49 |
|
Prime Factors |
7 |
|
Prime Factorization |
72 |

How to Find the Factors of 49
The factors can be found using different methods.
Methods to find the factors of 49 are:
- Multiplication Method
- Division Method
- Prime Factor and Prime Factorization
- Factor Tree

Finding Factors Using Multiplication Method
The multiplication method involves finding pairs of numbers that give 49 as their product.
A step-by-step process:
Step 1: Find the possible numbers whose product will give 49.
Step 2: The numbers found should have 49 as the product. These numbers are its factors.
Step 3: Rewrite the particular numbers and pair them.
List of numbers whose product is 49:
1 × 49 = 49
7 × 7 = 49

So the pair of numbers whose product is 49 are (1,49) and (7,7).
Explore Our Programs



Finding Factors Using Division Method
The division method helps to find the dividend and quotient as the factors of 49
Step-by-step process:
Step 1: Always start the division with the number 1. Since every number is divisible by 1, the number 1 will always be a factor. Example: 49÷1 = 49
Step 2: Move to the next integer and see if the number gets divided completely. Both divisor and quotient are the factors.
Picture showing the division process:

Here, 1 and 7 are the divisors and 49 is the dividend. 7 and 49 are the quotients. The remainder is zero.
Overview of factors of 49 using the Division Method.

Prime Factors and Prime Factorization
Multiplying prime numbers to get the given number as their product is called prime factors. Prime factorization is the process of breaking down the number into its prime factors.
Prime Factors of 49
Number 49 has only 7 as its prime factor.
To find the prime factor of 49:
Divide 49 with the prime number 7
49÷7 = 7
7÷7 = 1
Prime Factorization of 49
Prime Factorization helps to express the prime factors in their exponential form. Prime Factorization breaks down the prime factors of 49. Prime Factorization of 49 is expressed as 72

Factor Tree
The prime factorization is visually represented using the factor tree. It helps to understand the process easily. In this factor tree, each branch splits into prime factors.
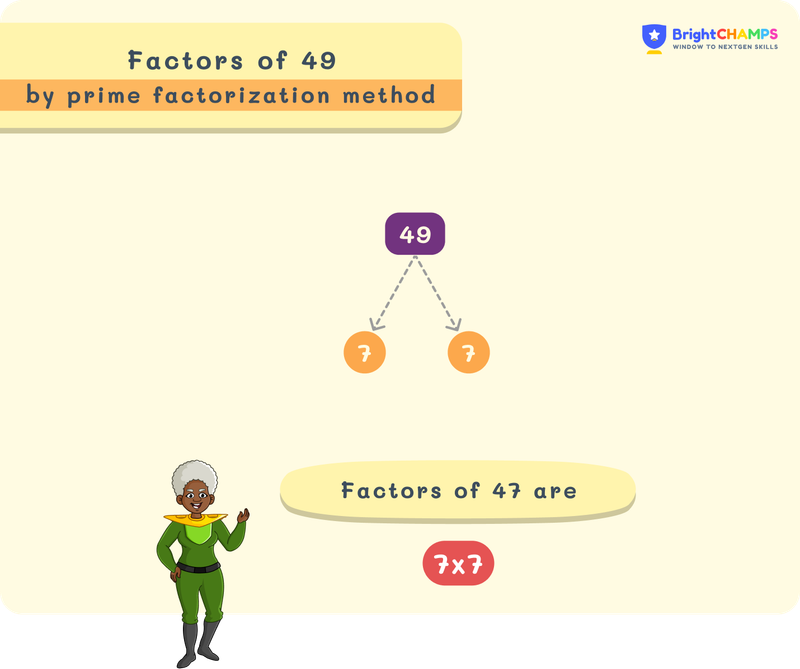
Factor Pairs
Factors of 49 can be written in both positive pairs and negative pairs. The factor pairs are a set of two factors. Their product will be equal to the number given.
- Positive factor pairs: (1,49), (7,7)
- Negative factor pairs: (-1,-49), (-7,-7)

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them in Factors of 49
Learn about the common mistakes that can occur. Solutions to solve the common mistakes are given below.

Solved examples on Factors of 49

Problem 1
Is it possible to consider 2 as a factor of 49?

No, 2 can never be a factor of 49.
Explanation
2 is not a factor of 49 because it cannot divide 49 completely, it leaves a remainder.

Problem 2
All the factors of 49 are odd. What will be the product of all the factors?

The product is 343.
Explanation
The factors of 49 are 1, 7, and 49. Multiplying these factors will give the product 343.
1 × 49 = 49
7 × 7 = 49

Problem 3
Identify the factor pair whose sum is 50

The factor pair is (1,49)
Explanation
When the factor pair (1,49) is added (1 + 49), we get 50 as the sum.

Problem 4
What is the GCF of 49 and 7?

The GCF is 7.
Explanation
From the factors of 49 and 7, choose the greatest common factor. Factors of 49 are 1, 7, and 49. Factors of 7 are 1 and 7.

Problem 5
Can you count the total negative factors of 49?

Yes, there are 3 negative factors.
Explanation
The negative factors are -1, -7, and -49.


FAQs on Factors of 49
1.Is 49 a factor or a multiple of 7?
2.Is 21 a factor of 49?
3.Is 49 divisible by 7?
4.What is the 7-rule division?
5.Is 175 divisible by 175?

Glossary
Dividend: Number that has to be divided
Quotient: The result we get after dividing a number with another
Odd numbers: Numbers that are not divisible by 2.
Perfect squares: Numbers we get when the same number is multiplied twice.
Greatest Common Factor: The largest integer that divides two or more integers without any remainder
Multiples: The result we get when another number multiplies the given number.



Hiralee Lalitkumar Makwana
About the Author
Hiralee Lalitkumar Makwana has almost two years of teaching experience. She is a number ninja as she loves numbers. Her interest in numbers can be seen in the way she cracks math puzzles and hidden patterns.
Fun Fact
: She loves to read number jokes and games.



























