Summarize this article:
 2710 Learners
2710 LearnersLast updated on August 5, 2025
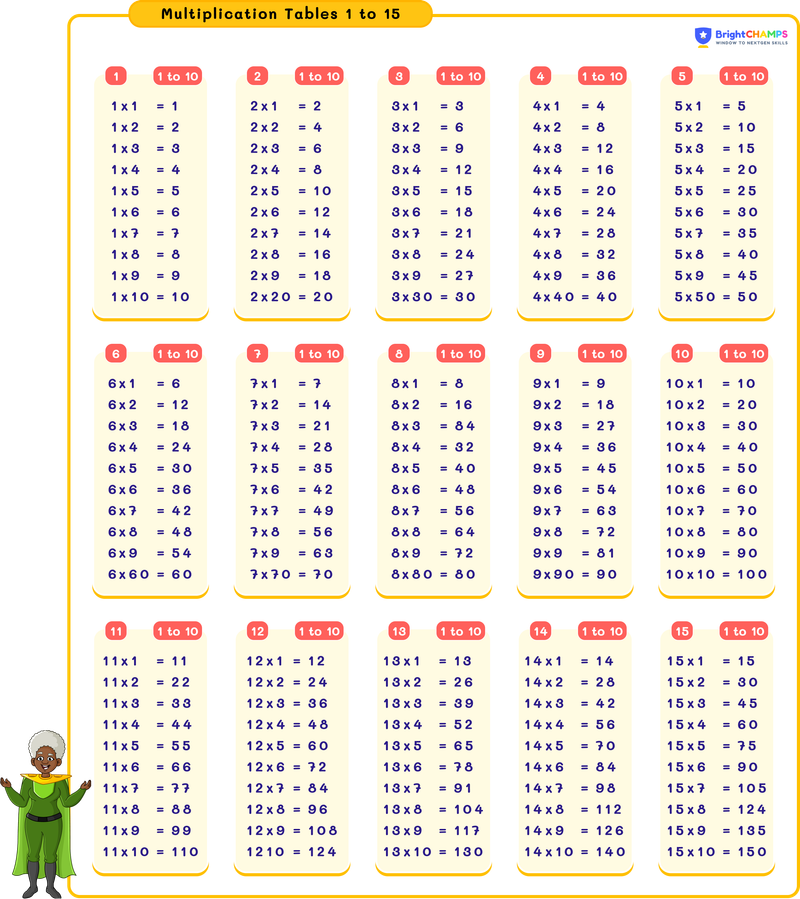
Tables from 1 to 15

A multiplication table is a table that helps us solve the result when we multiply numbers. Learning times tables help children understand multiplication, one of the foundational math operations applied to an algebraic system. Times tables can be applied for everyday math problems from counting money to understanding time. In this topic, we will discuss more about tables from 1 to 15.

Table of 1 to 5
Learning the tables from 1 to 5 will make math much easier, as it is the building blocks of multiplication. When you multiply by 1, you get the same number, and for 2 you are doubling it each time! Let's look into the tables from 1 to 5.

Table of 6 to 10
Now that you know the first five times tables, let's move on to the next set! These tables will help you multiply even faster. You’ll start noticing some interesting patterns, like in the tables of 10, just add zero after each number from 1 to 9. Such patterns will help you memorize times tables.

Table of 11-15
Let’s finish with the final set of the times tables! Learning these will elevate your understanding of multiplication. With the times table of 11 to 15, you’ll see how multiplication goes on with bigger numbers. And you get a hold of it eventually.
Explore Our Programs



Multiplication chart 1 to 15
Here’s a multiplication chart for numbers 1 to 15! Think of it like a map that shows how numbers are multiplied. It’s an easy and fun way to get all the answers right away so that you don’t have to do the math every time. With this chart, you can find the result of multiplying any number from 1 to 15 in a go! Let’s dive in and make multiplication simple and exciting.

Tips to memorize multiplication tables 1 to 15
- Kids might find times tables difficult at first, but it gets easier and super exciting with a few tricks. Here are some engaging tips and tricks to help kids learn multiplication tables, quicker and easier.
- Begin with easy times tables: Start with easier tables like 2,5,9 and 10. These have simple patterns that are followed, which makes it easier to memorize. Once you get a hang of these, you can move to the bigger numbers.
Example: In the table of 2, start with 2 and double the number as you go. 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20. Doubling makes this table easy to learn.
- Practice with real-life examples: Try to use real-life situations to get a better understanding of multiplication tables. For example, sharing pizza slices between a group of people.
- Identifying patterns: Each times table follows a pattern. Let's learn about these patterns. It will help and make it easier for you to memorize!
- For 2, 4, 8, 12, and 14: Start by doubling numbers. For the table of 2, just add 2 each time as mentioned above; for 4, double the 2’s table; for 8, double the 4’s table, and so on. The pattern is all about doubling numbers step by step.
- For 3, 6, 9, and 13: The 3’s table follows a pattern of adding 3 every time, and the 6’s table is just double of 3’s table. For the 9’s table, the one's digits count down from 9 to 0 in reverse order.
- For the 13’s table: start with 13 and keep adding 13 to each result, followed by a similar pattern.
- For 5, 10, 15: The 5’s table is easy since the numbers end in 0 or 5. For 10, just add a zero after the number, and for 15, remember that 15 × 1 is 15, 15 × 2 is 30, and so on – just keep adding 15.

Common mistakes and how to avoid them in tables From1 to 15
It’s normal to make mistakes while learning multiplication tables. Let’s look at some common mistakes kids make when learning multiplication tables and how to avoid them.

Math Tables From 1 to 15 Examples

Problem 1
A bus travels 50 kilometers per hour. How far will it travel in 8 hours?

The bus will travel 400 kilometers in 8 hours.
Explanation
Multiply the speed of the bus by the number of hours.
50 × 8 = 400
The bus will travel 400 kilometers in 8 hours.

Problem 2
Find the missing number: 15 × __ = 120.

The missing number is 8.
Explanation
Dividing 120 ÷ 15, we get 8
15 × 8 = 120.
Then we multiply 15 and 8, to get 120.

Problem 3
A book costs ₹120. How much will 5 such books cost?

The total cost for 5 books is ₹600.
Explanation
Multiply the price of one book by 5.
120 × 5 = 600
The total cost for 5 books is, ₹600.


FAQs on Tables From 1 to 15
1.Is 100 in the 15 times table?
2.How can one quickly verify if the number is in the 10 times table?
3.Check if 144 is in the 12 times table.
4.How do you identify patterns in the 5 times table?
5.Is 121 in the 13 times tables?

Important Glossaries for Tables 1 to 15
- Multiplicand: Multiplicand is the number you are multiplying with. For example, 7 × 5 = 35, the number 7 is the multiplicand and 5 is the multiplier.
- Multiplier: The number that tells you how many times the multiplicand should be multiplied. For example, in 7 × 4 = 28, the multiplier is 4 as we multiply 7 four times.
- Skip counting: Adding by the same number repeatedly. For example, skip counting by 5: 5, 10, 15, 20…
- Multiple: A number you get when you multiply a number by any integer. For example, 10 is a multiple of 5 because 5 × 2 is 10.



Seyed Ali Fathima S
About the Author
Seyed Ali Fathima S a math expert with nearly 5 years of experience as a math teacher. From an engineer to a math teacher, shows her passion for math and teaching. She is a calculator queen, who loves tables and she turns tables to puzzles and songs.
Fun Fact
: She has songs for each table which helps her to remember the tables

















