


 113 Learners
113 LearnersLast updated on May 26th, 2025

Multiples of 150

In math, multiples are the products we get when multiplying a number with other numbers. Multiples play a key role in construction and design, counting groups of items, sharing resources equally, and managing time effectively. In this topic, we will learn the essential concepts of multiples of 150.
What are the Multiples of 150?
Now, let us learn more about multiples of 150. Multiples of 150 are the numbers you get when you multiply 150 by any whole number, including zero. Each number has an infinite number of multiples, including a multiple of itself.
In multiplication, a multiple of 150 can be denoted as 150 × n, where ‘n’ represents any whole number (0, 1, 2, 3,…). So, we can summarize that:
Multiple of a number = Number × Any whole number
For example, multiplying 150 × 1 will give us 150 as the product. Multiples of 150 will be larger or equal to 150.
List of First 20 Multiples of 150
Multiples of 150 include the products of 150 and an integer. Multiples of 150 are divisible by 150 evenly. The first few multiples of 150 are given below:
| TABLE OF 150 (1-10) | |
|---|---|
| 150 x 1 = 150 | 150 x 6 = 900 |
| 150 x 2 = 300 | 150 x 7 = 1050 |
| 150 x 3 = 450 | 150 x 8 = 1200 |
| 150 x 4 = 600 | 150 x 9 = 1350 |
| 150 x 5 = 750 | 150 x 10 = 1500 |
| TABLE OF 150 (11-20) | |
|---|---|
| 150 x 11 = 1650 | 150 x 16 = 2400 |
| 150 x 12 = 1800 | 150 x 17 = 2550 |
| 150 x 13 = 1950 | 150 x 18 = 2700 |
| 150 x 14 = 2100 | 150 x 19 = 2850 |
| 150 x 15 = 2250 | 150 x 20 = 3000 |
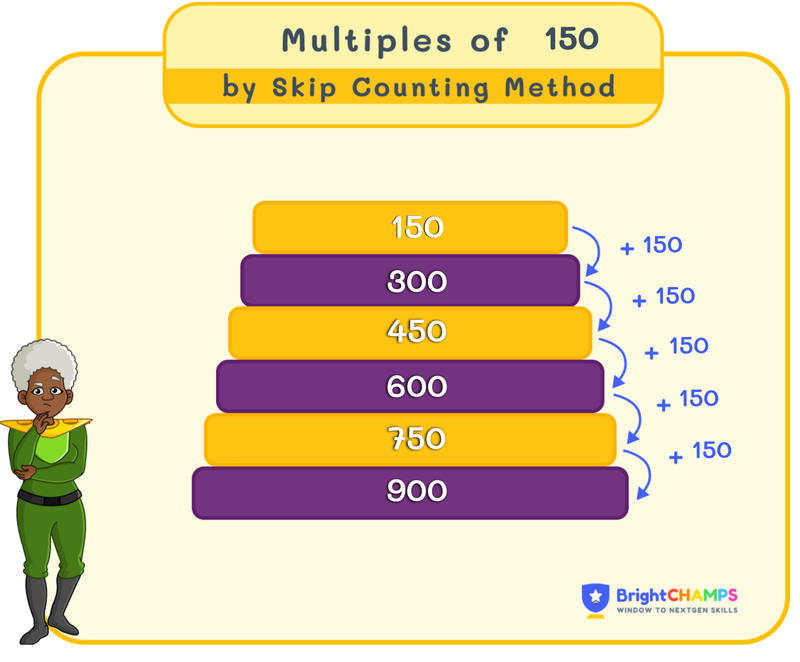
Now, we know the first few multiples of 150. They are 0, 150, 300, 450, 600, 750, 900, 1050, 1200, 1350, 1500,...
Operations with Multiples of 150
Understanding the multiples of 150 helps solve mathematical problems and boost our multiplication and division skills. When working with multiples of 150, we need to apply it to different mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
Sum of first 5 Multiples of 150:
150, 300, 450, 600, and 750 are the first five multiples of 150. When multiplying 150 from 1 to 5 we get these numbers as the products.
So, the sum of these multiples is:
150 + 300 + 450 + 600 + 750 = 2250
When we add the first 5 multiples of 150 the answer will be 2250.
Subtraction of first 5 Multiples of 150:
While we do subtraction, it improves our comprehension of how the value decreases when each multiple is subtracted from the previous one. 150, 300, 450, 600, and 750 are the first five multiples of 150. So, let us calculate it as given below:
150 - 300 = -150
-150 - 450 = -600
-600 - 600 = -1200
-1200 - 750 = -1950
Hence, the result of subtracting the first 5 multiples of 150 is -1950.
Average of first 5 Multiples of 150:
To calculate the average, we need to identify the sum of the first 5 multiples of 150, and then divide it by the count, i.e., 5. Because there are 5 multiples presented in the calculation. Averaging helps us to understand the concepts of central tendencies and other values. We know the sum of the first 5 multiples of 150 is 2250.
150 + 300 + 450 + 600 + 750 = 2250
Next, divide the sum by 5:
2250 ÷ 5 = 450
450 is the average of the first 5 multiples of 150.
Product of First 5 Multiples of 150:
The product of given numbers is the result of multiplying all of them together. Here, the first 5 multiples of 150 include: 150, 300, 450, 600, and 750. Now, the product of these numbers is:
150 × 300 × 450 × 600 × 750 = 13,500,000,000,000
The product of the first 5 multiples of 150 is 13,500,000,000,000.
Division of First 5 Multiples of 150:
While we perform division, we get to know how many times 150 can fit into each of the given multiples. 150, 300, 450, 600, and 750 are the first 5 multiples of 150.
150 ÷ 150 = 1
300 ÷ 150 = 2
450 ÷ 150 = 3
600 ÷ 150 = 4
750 ÷ 150 = 5
The results of dividing the first 5 multiples of 150 are: 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5.

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them in Multiples of 150
While working with multiples of 150, we make common mistakes. Identifying these errors and understanding how to avoid them can be helpful. Below are some frequent mistakes and tips to avoid them:

Multiples of 150 Examples

Problem 1
A factory produces 150 gadgets every day. The factory operates 5 days a week. How many gadgets does the factory produce in 4 weeks?

3000 gadgets
Explanation
The factory produces 150 gadgets each day. To find the total production over 4 weeks, calculate the number of gadgets produced per week and then multiply by 4 weeks.
- Gadgets produced per day = 150
- Number of days per week = 5
- Number of weeks = 4
150 × 5 = 750 gadgets per week
750 × 4 = 3000 gadgets in 4 weeks
The factory produces 3000 gadgets in 4 weeks.

Problem 2
A construction company is laying down 150 meters of pipeline every day. If they continue at this rate, how many meters of pipeline will they have laid down after 10 days?

1500 meters
Explanation
To determine the total pipeline laid down after 10 days, multiply the daily progress by the number of days.
- Pipeline laid per day = 150 meters
- Number of days = 10
150 × 10 = 1500 meters
The company lays down 1500 meters of pipeline in 10 days.

Problem 3
At a printing press, 150 copies of a magazine are printed in an hour. How many copies will be printed in an 8-hour workday?

1200 copies
Explanation
Calculate the total number of copies printed in a full workday by multiplying the hourly output by the total hours worked.
- Copies printed per hour = 150
- Workday length = 8 hours
150 × 8 = 1200 copies
1200 copies are printed in an 8-hour workday.

Problem 4
A gardener plants 150 flowers in a row. If he plants rows of flowers every day for a week, how many flowers will he have planted by the end of the week?

1050 flowers
Explanation
Determine the total number of flowers planted by multiplying the number of flowers per row by the days in a week.
- Flowers per row = 150
- Days in a week = 7
150 × 7 = 1050 flowers
The gardener plants 1050 flowers in a week.

Problem 5
A charity organization packs 150 meals each day for distribution. How many meals will they have prepared after 6 days?

900 meals
Explanation
Find the total number of meals prepared over 6 days by multiplying the daily output by the number of days.
- Meals prepared per day = 150
- Number of days = 6
150 × 6 = 900 meals
The organization prepares 900 meals in 6 days.


FAQs on Multiples of 150
1.How do you find the multiples of 150?
2.What is the LCM of 10 and 150?
3.What are the real-life applications of Multiples of 150?
4.Are multiples of 150 finite or infinite?
5.Is there any odd multiple of 150?
Important Glossary for Multiples of 150
- Multiple: A multiple represents the product of a number that may be multiplied by an integer. For example, multiples of 150 include 150, 300, 450, 600, etc.
- Number pattern: This refers to how numbers are listed. It should follow a certain sequence. Multiples of 150 are the numbers that consist of the number pattern of 150.
- Even number: An even number refers to any number that can be divided by 2 without leaving any remainder. The last digits of even numbers are 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8. All multiples of 150 are even numbers.
- Divisor: It refers to any number by which another number can be divided without leaving any remainder. 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 25, 30, 50, 75, and 150 are the divisors of 150.
- LCM (Least Common Multiple): The smallest common multiple shared by a set of numbers. For example, the LCM of 10 and 150 is 150.
Explore More multiplication-tables
 Previous to Multiples of 150
Previous to Multiples of 150


Seyed Ali Fathima S
About the Author
Seyed Ali Fathima S a math expert with nearly 5 years of experience as a math teacher. From an engineer to a math teacher, shows her passion for math and teaching. She is a calculator queen, who loves tables and she turns tables to puzzles and songs.

Fun Fact
: She has songs for each table which helps her to remember the tables



