
 170 Learners
170 LearnersLast updated on May 26th, 2025

611 in Roman Numerals

Roman numerals are a way of expressing numbers using symbols like I, V, X, L, C, D, and M. These numerals are employed in various contexts such as royal titles, book names, sequences, and more. Here, we will discuss Roman numerals, their rules, and provide examples.
What is 611 in Roman Numerals?
Royal titles, such as Henry I, Henry II, etc., often use Roman numerals. But what do these symbols (I and II) represent? They are Roman numerals. In earlier times, people counted using fingers, sticks, bones, etc.
As life became more complex, a standardized counting system was needed, leading to the development of Roman numerals by the ancient Romans. The symbols used include I (1), V (5), X (10), L (50), C (100), D (500), and M (1000).
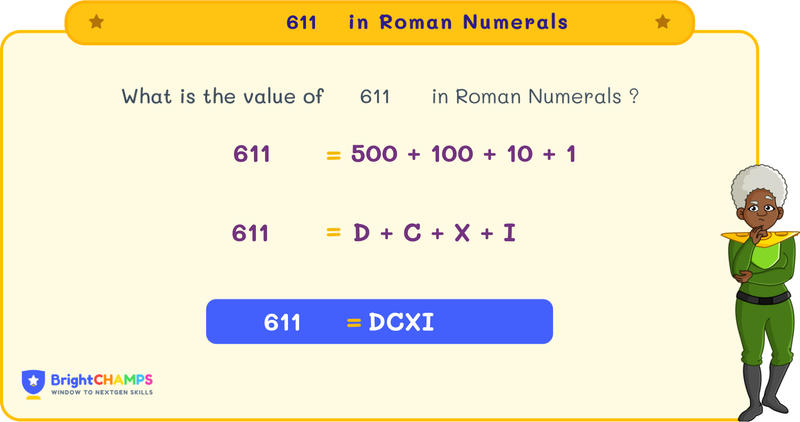
In Roman numerals, 611 is represented as DCXI. Here, D represents 500, C is 100, X is 10, and I is 1. Let’s learn more about Roman numerals and how we write them.
Struggling with Math?
Get 1:1 Coaching to Boost Grades Fast !

Basic Rules for 611 in Roman Numerals
There are basic rules for writing numbers in Roman numerals. Let's discuss some essential rules to remember when converting numbers to Roman numerals.
Rule 1: Addition Method
The addition method is used when a smaller number is placed after a larger number. For example, XI → X + I → 10 + 1 = 11.
Rule 2: Repetition Method
Certain Roman numerals can be repeated up to three times to indicate addition. For example, III → 3.
Rule 3: Subtraction Method
If a smaller number precedes a larger number, subtract the smaller from the larger. For example, IX → X - I → 10 - 1 = 9.
Rule 4: Limitation Rule Symbols
cannot be repeated more than three times, and certain symbols like V, L, and D cannot be repeated. For example, we don't write VV for 10; instead, we use X. Similarly, we write 8 as VIII, not IIIIIIII.
How to Write 611 in Roman Numerals
Let’s learn how to write 611 in Roman numerals using different methods.
- By Expansion Method
- By Grouping Method
611 in Roman Numeral by Expansion Method
In the expansion method, a number is broken down based on its place values. Here's how to write 611 in Roman numerals using this method.
Step 1: Break down the number based on place value: ones, tens, hundreds, etc. For 611, we write it as 600 + 10 + 1.
Step 2: Convert each part into Roman numerals:
600 in Roman numerals - DC
(D = 500, C = 100)
10 in Roman numerals - X
1 in Roman numerals - I
Step 3: Combine the Roman numerals. Therefore, 611 in Roman numerals is DC (500 + 100) + X (10) + I (1) = DCXI.
611 in Roman Numeral by Grouping Method
When writing large numbers in Roman numerals, numbers are grouped. To write 611 in Roman numerals, group it as 600 + 10 + 1.
- 600 in Roman numerals - DC
- 10 in Roman numerals - X
- 1 in Roman numerals - I
So, 611 is written as DCXI in Roman numerals.

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them in 611 Roman Numerals
Students often make mistakes when writing numbers in Roman numerals. To master Roman numerals, learn common mistakes and ways to avoid them.
Level Up with a Math Certification!
2X Faster Learning (Grades 1-12)


611 in Roman Numerals Examples

Problem 1
Calculate the sum of DCXI and XL.

The sum of DCXI and XL is DCLI.
Explanation
DCXI is 611 and XL is 40. The sum of 611 and 40 is 651. 651 in Roman Numerals is written as DCLI.

Problem 2
A historian has a collection of DCXI ancient artifacts and wants to distribute them equally among X museums. How many artifacts will each museum receive?

Each museum will receive LXI artifacts.
Explanation
To find the number of artifacts each museum receives, divide the total number of artifacts by the number of museums:
DCXI / X.
DCXI is 611 and X is 10.
Therefore, 611 / 10 = 61. 61 in Roman numerals is written as LXI.

Problem 3
Find the difference between DCLX and DCXI.

The difference between DCLX and DCXI is XLIX.
Explanation
The difference of two numbers is the value obtained by subtracting one from the other.
DCLX is 660 and DCXI is 611.
660 - 611 = 49. 49 in Roman Numerals is written as XLIX.

Problem 4
A scholar translated DCXI pages of an ancient manuscript and wants to review LIX pages each week. How many weeks will it take to review the entire manuscript?

It will take XI weeks to review the entire manuscript.
Explanation
To find the number of weeks, divide the total number of pages by the number of pages reviewed each week:
DCXI / LIX.
DCXI is 611 and LIX is 59.
Therefore, 611 / 59 = 11. 11 in Roman numerals is written as XI.

Problem 5
Express the result of 611 - 273 in Roman numerals.

The result of 611 - 273 in Roman numerals is CCCXXXVIII.
Explanation
First, calculate the difference: 611 - 273 = 338. Then convert 338 into Roman numerals.
338 = 300 + 30 + 8.
In Roman numerals, this is CCCXXXVIII.

Turn your child into a math star!
#1 Math Hack Schools Won't Teach!


FAQs on 611 in Roman Numerals
1.What is 610 in Roman numerals?
2.How to write 611 in Roman numerals?
3.What is 616 in Roman Numerals?
4.Is DCXI a prime number?
5.What are the multiples of 611?
6.How can children in United States use numbers in everyday life to understand 611 in Roman Numerals?
7.What are some fun ways kids in United States can practice 611 in Roman Numerals with numbers?
8.What role do numbers and 611 in Roman Numerals play in helping children in United States develop problem-solving skills?
9.How can families in United States create number-rich environments to improve 611 in Roman Numerals skills?
Struggling with Math?
Get 1:1 Coaching to Boost Grades Fast !

Important Glossaries for 611 in Roman Numerals
- Addition Rule: Used when a large numeral is followed by a smaller one, adding their values. For example, DCXI = D + C + X + I = 500 + 100 + 10 + 1 = 611.
- Grouping Method: The number is grouped based on place value and each group is converted into Roman numerals. For example, 611 = 600 + 10 + 1 = DCXI.
- Repetition Rule: Certain symbols (I, X, C, M) can be repeated up to three times in the Roman numeric system. For example, III = 3.
- Subtraction Rule: Applied when a smaller numeral precedes a larger one, subtracting the smaller value from the larger. For example, IV = 5 - 1 = 4.
- Place Value: The value of the digit based on its position within a number. For example, in 611, the place values are 600, 10, and 1.
Explore More numbers
![Important Math Links Icon]() Previous to 611 in Roman Numerals
Previous to 611 in Roman Numerals
![Important Math Links Icon]() Next to 611 in Roman Numerals
Next to 611 in Roman Numerals
About BrightChamps in United States


Hiralee Lalitkumar Makwana
About the Author
Hiralee Lalitkumar Makwana has almost two years of teaching experience. She is a number ninja as she loves numbers. Her interest in numbers can be seen in the way she cracks math puzzles and hidden patterns.
Fun Fact
: She loves to read number jokes and games.




