Summarize this article:
 388 Learners
388 LearnersLast updated on 5 August 2025
Table of 431

The table of 431 is one of the essential multiplication tables. Learning the 431 times table helps in enhancing mental ability. Understanding the 431 times table builds numerical fluency. Let’s understand more about Table of 431.

What is a multiplication table of 431?
The multiplication table of 431 is a chart of multiples of 431 and follows a unique pattern. Let’s understand more.
Table of 431 consists of multiples of 431, a list with a structure that helps calculate the sums of 431.
Repeated addition of 431 is followed throughout the table and keeps increasing as 431, 862, 1293, 1724, 2155, 2586, 3017, 3448, 3879, 4310…
The digits at the one’s place of the product of Table of 431 do not follow a repetitive pattern due to the larger base number.
Products of the table of 431 result in larger numbers and are essential for advanced calculations.
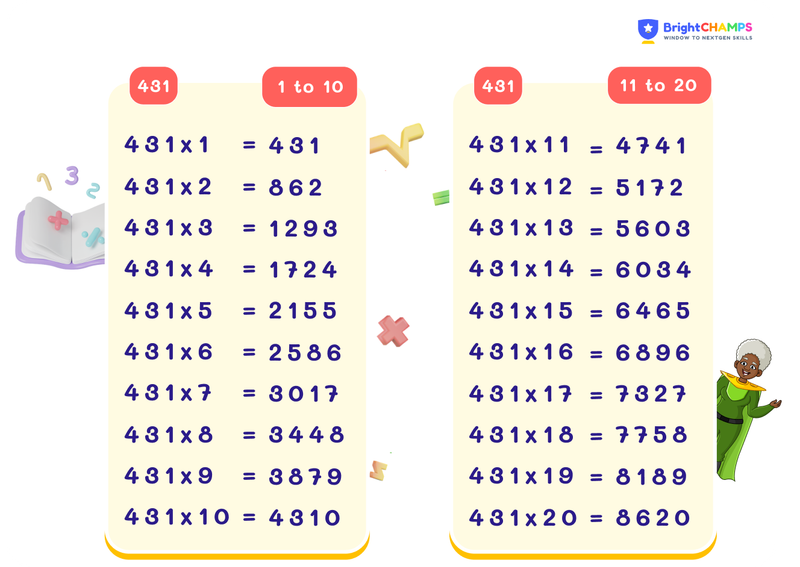

Chart of Table of 431
Table of 431 may be hard and takes more time to understand. Practicing it regularly can make it easy.
Table of 431 for the multiples 1 to 10 and 11 to 20 are listed below.
| TABLE OF 431 (1-10) | |
|---|---|
|
431 x 1 = 431 |
431 x 6 = 2586 |
|
431 x 2 = 862 |
431 x 7 = 3017 |
|
431 x 3 = 1293 |
431 x 8 = 3448 |
|
431 x 4 = 1724 |
431 x 9 = 3879 |
|
431 x 5 = 2155 |
431 x 10 = 4310 |
| TABLE OF 431 (11-20) | |
|---|---|
|
431 x 11 = 4741 |
431 x 16 = 6896 |
|
431 x 12 = 5172 |
431 x 17 = 7327 |
|
431 x 13 = 5603 |
431 x 18 = 7758 |
|
431 x 14 = 6034 |
431 x 19 = 8189 |
|
431 x 15 = 6465 |
431 x 20 = 8620 |

Tips and Tricks for the Multiplication Table of 431
Multiplication tables are fundamental for developing math skills. Some tips and tricks are listed below.
The Table of 431 has a consistent numerical pattern, and understanding this pattern makes it easier to learn the table. While the numbers grow large, focusing on place values and repetitive addition simplifies learning.
Breaking up multiplication into smaller numbers makes it easy. For example, to calculate 431 × 13, it can be broken down into:
431 × 10 + 431 × 3 = 4310 + 1293 = 5603
The Table of 431 can also be practiced using the repeated addition method: 431, 862, 1293, 1724, 2155, and so on. Repeated addition helps reinforce each step while memorizing.
When multiplying 431 by smaller numbers, recognize patterns in the tens and hundreds places to reduce errors. For example, 431 × 4 = 1724 can be verified by adding 431 four times:
431 + 431 + 431 + 431 = 1724
Using the table of smaller numbers, such as Table of 1 or 2, can help cross-check results. For example, 431 × 2 = 862, and this can be validated through basic addition.
The tips and tricks above will help you with the 431 times table. The common mistakes and the solved examples show where to look out for errors and how to solve problems efficiently.

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them in 431 Times Tables
Committing mistakes while learning the Table of 431 is common. You can avoid making these mistakes by being more careful in the areas mentioned below.

Table of 431 Solved Examples

Problem 1
Sarah plans to host a party and plans to give a gift box to each of her 431 friends. Each gift box will contain 5 chocolates. How many chocolates does Sarah need to buy in total?

2,155 chocolates
Explanation
Using the Table of 431,
431×5=2,155431
So, Sarah needs to buy 2,155 chocolates.

Problem 2
At Simon’s house, 431 rows containing 7 books are arranged on a shelf. How many books does he have in total?

3,017 books
Explanation
From the Table of 431,
431×7=3,017431
Thus, Simon has 3,017 books in total.

Problem 3
With the help of Table of 431, check if 431 times 4 minus 600 is 1,124 or not.

Yes, it is 1,124.
Explanation
First, calculate 431×4431
431×4=1,724431
Now subtract 600:
1,724−600=1,1241,724 - 600 = 1,1241,724−600=1,124
So, the final answer is indeed 1,124.


FAQs on Times Table of 431
1.What is the multiplication table of 431?
2.What is the trick to learn the 431 times table?
3.Why are all the products in the table of 431 odd or even numbers?
4.How do I use the multiplication table of 431 in the division?
5.Define the relationship between the products of 431 and the products of 215.5?
6.What is the relationship between the 431 times table and powers of 2?
7.Can I practice the 431 times table using puzzles or quizzes?
8.Can learning the Multiplication Table influence creativity in solving Table of 431 challenges for kids in United Arab Emirates?
9.What role does brain development play in mastering the Multiplication Table and Table of 431 among early learners in United Arab Emirates?
10.How do language and cultural differences in United Arab Emirates affect the way children learn the Multiplication Table and Table of 431?
11.How can poems help children in United Arab Emirates memorize the Multiplication Table and Table of 431?

Important Glossaries for Table of 431
Factor: Factors are numbers that, when multiplied together, result in a product.
Multiples: Multiples are numbers obtained by multiplying a given number by whole numbers.
Repeated Addition: A method of adding the same number multiple times to achieve the product of a multiplication.
Place Value: The numerical value assigned to a digit based on its position in a number (ones, tens, hundreds, etc.).
Carryover: The value carried to the next digit column during multiplication when a product exceeds 9 in a single column.

Explore More multiplication-tables


Seyed Ali Fathima S
About the Author
Seyed Ali Fathima S a math expert with nearly 5 years of experience as a math teacher. From an engineer to a math teacher, shows her passion for math and teaching. She is a calculator queen, who loves tables and she turns tables to puzzles and songs.
Fun Fact
: She has songs for each table which helps her to remember the tables




