


 163 Learners
163 LearnersLast updated on May 26th, 2025

Table of 708

A times table is a chart that shows the results of multiplying a number with whole numbers. Learning the times table will help kids understand multiplication. We use an algebraic system to define multiplication operations, construction, estimation, schoolwork, exams, and more. In this topic, we will learn about the table of 708.
What is the multiplication table of 708?
Multiplication was used by people over 4000 years ago. Babylonians were considered the first to use it in clay tablets. Multiplication tables are created as a result of people's search for easier ways to solve problems. Learning multiplication tables has numerous advantages. Kids can respond quickly if they know their times table. It also helps to enhance their comprehension skills. Being more familiar with the tables improves children's memory and confidence.
Multiplying the whole number (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and so on) by 708 gives the product of the multiplication table of 708.
Here are some examples:
708 × 1 = 708
708 × 2 = 708 + 708 = 1416
708 × 3 = 708 + 708 + 708 = 2124
708 × 4 = 708 + 708 + 708 + 708 = 2832
708 × 5 = 708 + 708 + 708 + 708 + 708 = 3540
708, 1416, 2124, 2832, 3540, and so on are multiples of 708.
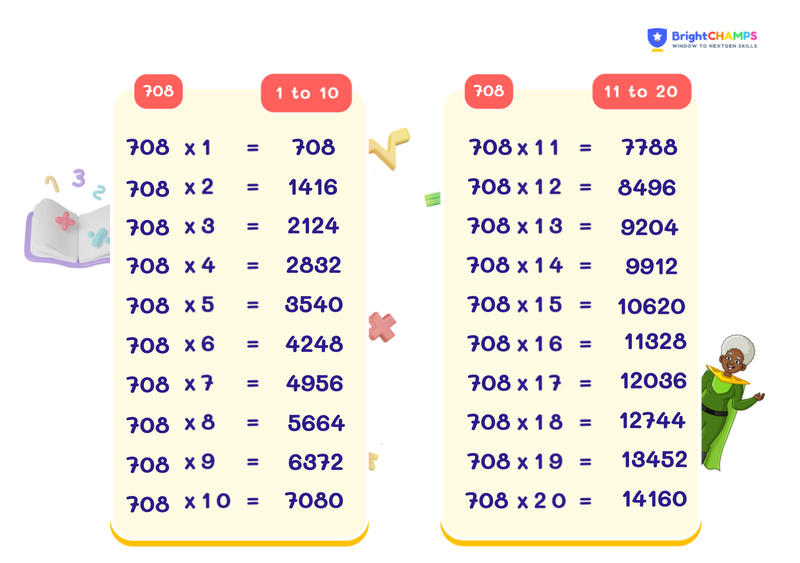
708 Times Table Chart
The 708 times table chart shows the multiples of 708. Every result in the chart is obtained by multiplying 708 with other whole numbers, like 1 to 10, and so on.
For example:
708 × 10 = 7080
708 × 11 = 7788
708 × 12 = 8496, and so on.
| TABLE OF 708 (1-10) | |
|---|---|
|
708 x 1 = 708 |
708 x 6 = 4248 |
|
708 x 2 = 1416 |
708 x 7 = 4956 |
|
708 x 3 = 2124 |
708 x 8 = 5664 |
|
708 x 4 = 2832 |
708 x 9 = 6372 |
|
708 x 5 = 3540 |
708 x 10 = 7080 |
| TABLE OF 708 (11-20) | |
|---|---|
|
708 x 11 = 7788 |
708 x 16 = 11328 |
|
708 x 12 = 8496 |
708 x 17 = 12036 |
|
708 x 13 = 9204 |
708 x 18 = 12744 |
|
708 x 14 = 9912 |
708 x 19 = 13452 |
|
708 x 15 = 10620 |
708 x 20 = 14160 |
Tips and Tricks for the Multiplication Table of 708
Understanding the multiplication table of 708 can be challenging because of the larger number involved. But with the tips and tricks, it becomes easier. Let’s look into some:
Break the numbers into smaller parts:
Breaking the numbers into smaller parts will make it easy to learn multiplication.
For example: 708 × 4
Here, 708 can break into 700 + 8
(700 × 4) + (8 × 4) = 2800 + 32
= 2832.
Use flashcards:
On one side of the flashcard, write the multiplication problems.
For example:
Front: 708 × 3
Back: 2124.
Repeated patterns:
The unit digits in the 708 times table repeat every 5 multiples.
For example: The unit digits repeat in the cycle: 8, 6, 4, 2, 0. After every 5 multiples, the cycle restarts.

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them in Table of 708
While working on the table of 708, it's common for kids to make some errors. Here are some common mistakes that kids make and the tips on how to avoid them.

Table of 708 Examples

Problem 1
A publishing company prints 708 pages for a book, and each book needs 708 pages. How many books can be printed with 708 pages?

1 book.
Explanation
Since each book requires 708 pages, and there are 708 pages available, exactly 1 book can be printed. For example: 708 × 1 = 708.

Problem 2
A concert hall sells tickets for a music show. Each ticket costs 708 units. If the hall sells 7 tickets, how much revenue will they generate?

4956 units.
Explanation
To find the total revenue from ticket sales, multiply the ticket price (708) by the number of tickets sold (7):
708 × 7 = 4956 units.

Problem 3
A library has 708 bookshelves, and each shelf can hold 12 books. Calculate the total number of books that can be stored in the library.

8496 books.
Explanation
To find the total capacity of the library, multiply the number of shelves (708) by the number of books per shelf (12):
708 × 12 = 8496 books.

Problem 4
A landscaping company plants 708 meters of hedges each day. How many meters of hedges will be planted in 15 days?

10,620 meters.
Explanation
To calculate the total length of hedges planted in 15 days, multiply the daily planting length (708 meters) by the number of days (15):
708 × 15 = 10,620 meters.

Problem 5
A factory employs 708 workers, and each worker produces 6 widgets per day. What is the total number of widgets produced by the workers in one day?

4248 widgets.
Explanation
The total production of widgets in a day is calculated by multiplying the number of workers (708) by the number of widgets each worker produces (6):
708 × 6 = 4248 widgets.


FAQs on Table of 708
1.What are the factors of 708?
2.What are the multiples of 708?
3.How can kids practice the table of 708?
4.What is the pattern of the table of 708?
5.Is 708 a prime number?
Important Glossaries for Multiplication Table of 708
Multiplication: A mathematical operation of scaling one number by another.
Product: The result obtained by multiplying two numbers.
Factors: Numbers that are multiplied together to get another number.
Multiple: A number that can be divided by another number without a remainder.
Placeholder: A symbol or digit that holds a place for another digit in a number, often zero in multiplication.
Explore More multiplication-tables
 Previous to Table of 708
Previous to Table of 708


Seyed Ali Fathima S
About the Author
Seyed Ali Fathima S a math expert with nearly 5 years of experience as a math teacher. From an engineer to a math teacher, shows her passion for math and teaching. She is a calculator queen, who loves tables and she turns tables to puzzles and songs.

Fun Fact
: She has songs for each table which helps her to remember the tables



