Summarize this article:
 334 Learners
334 LearnersLast updated on August 5, 2025
52 in Roman Numerals

Roman numerals are a way of expressing numbers using symbols. I, V, X, L, C, D, and M are the symbols used. Roman Numerals are used in royal titles, book names, sequences, and so on. Here we will discuss Roman Numerals, rules, and examples.

What is 52 in Roman Numerals?
The royal titles, such as Henry I, Henry II, and so on, use Roman Numerals. Have you noticed the names and wondered what these symbols (I and II) represented? Those are the Roman Numerals. In ancient times, people counted using fingers, sticks, bones, etc. As life became more complex, a standard form was required to count. Ancient Romans used the Roman Numeral system for counting. I (1), V (5), X (10), L (50), C (100), D (500), and M (1000) are the symbols used to count.
In Roman Numerals, we use LII to represent 52, where L is 50 and II is 2. Let’s learn more about Roman numerals and how we write them.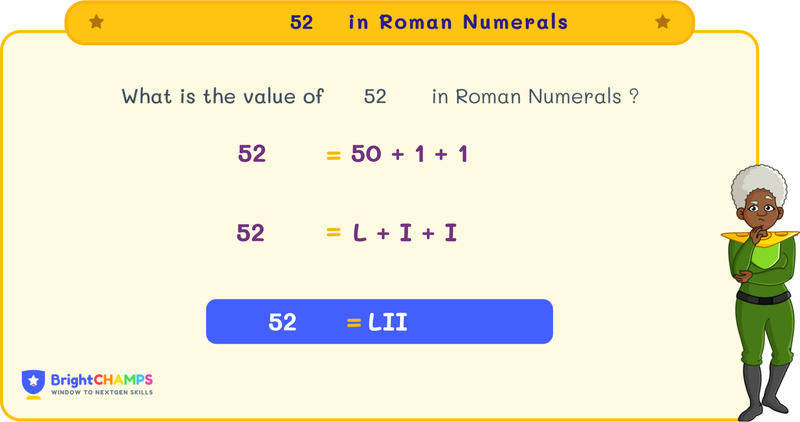

Basic Rules for 52 in Roman Numerals
There are certain basic rules to write a number in Roman Numerals. In this section, let’s discuss some basic rules that need to be remembered when writing a number in Roman numerals.
Rule 1: Addition Method
The addition method is used when a smaller number is placed after a larger number. For example, LII → L + II → 50 + 2 = 52
Rule 2: Repetition Method
To write a large number, certain Roman Numerals can be repeated up to three times. III → 3.
Rule 3: Subtraction Method
If a smaller number precedes a larger number in Roman Numerals, we subtract the smaller number from the larger one. For example, IX → X - I → 10 - 1 = 9
Rule 4: Limitation Rule
Symbols cannot be repeated more than three times, and some symbols like V, L, and D cannot be repeated. For example, we write 10 as X instead of VV, and 8 as VIII, not IIIIIIII.

How to Write 52 in Roman Numerals
Let’s now learn how to write 52 in Roman Numerals. Follow these methods to write the number in Roman Numerals.
- By Expansion Method
- By Grouping Method
Explore Our Programs



52 in Roman Numeral by Expansion Method
In the expansion method, based on the place value, the number is broken down. In this section, we will learn how to write 52 in Roman numerals using the expansion method.
To write 52 in Roman Numerals, follow these steps:
Step 1: Break the number based on place value. Place values are ones, tens, hundreds, etc.
For 52, we write it as 50 + 2
Step 2: Convert the number into Roman Numerals
50 in Roman Numeral — L
2 in Roman Numeral — II
Step 3: Combine the Roman Numerals together.
Therefore, 52 in Roman Numeral is L (50) + II (2) = LII

52 in Roman Numeral by Grouping Method
When writing a large number into a Roman Numeral, we group the number. To write 52 in Roman Numeral, we group 52 as 50 + 2.
50 in Roman Numeral — L
2 in Roman Numeral — II
So, 52 is written as LII in Roman Numerals.

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them in 52 Roman Numerals
Students often make mistakes when writing numbers in Roman Numerals. To master Roman Numerals, we can learn a few common mistakes and the ways to avoid them.

52 in Roman Numerals Examples

Problem 1
A historian finds a manuscript that mentions the dates of two significant events: XXV and XXVII years after the founding of a city. Calculate the total number of years after the founding of the city when both events are considered together.

The total number of years is LII.
Explanation
XXV = 25
XXVII = 27
The total number of years is 25 + 27 = 52.
52 in Roman numerals is LII.

Problem 2
An ancient Roman architect designed a building with a total of CCLX columns, arranged in groups of V columns per row. How many rows of columns are there?

There are LII rows of columns.
Explanation
To find the number of rows, divide the total number of columns by the number of columns per row:
CCLX = 260
V = 5
260 / 5 = 52
52 in Roman numerals is LII.

Problem 3
A collector has a series of rare coins, with the oldest dating back to the year MCMXLVIII and the newest to the year MM. Determine the number of years covered by the collection.

The collection covers LII years.
Explanation
MCMXLVIII = 1948
MM = 2000
2000 - 1948 = 52
52 in Roman numerals is LII.

Problem 4
A historian is analyzing a document that lists the number of soldiers in two battalions as XV and XXXVII. Calculate the total number of soldiers in both battalions.

The total number of soldiers is LII.
Explanation
XV = 15
XXXVII = 37
The total number of soldiers is 15 + 37 = 52.
52 in Roman numerals is LII.

Problem 5
A library has a special collection of rare manuscripts, and it receives an additional shipment of manuscripts, bringing the total to LII. If the library initially had XXX manuscripts, how many manuscripts were in the shipment?

The shipment contained XXII manuscripts.
Explanation
Initial number of manuscripts = XXX = 30
Total after shipment = LII = 52
Number of manuscripts in the shipment = 52 - 30 = 22
22 in Roman numerals is XXII.


FAQs on 52 in Roman Numerals
1.What is 9 in Roman numerals?
2.How to write 52 in Roman numerals?
3.What is 16 in Roman Numerals?
4.Is LII a prime number?
5.What are the multiples of 52?

Important Glossaries for 52 in Roman Numerals
- Addition rule: The addition method is used when a large number is followed by smaller numerals, here the values are added. For example, LII = L + II = 50 + 2 = 52.
- Grouping method: Here, the given numbers are grouped based on their place value, and then we convert each group into its Roman numerals. For example, 52 = 50 + 2 = LII.
- Repetition rule: Certain symbols (I, X, C, M) in the Roman numeric system can be repeated only up to three times. For example, III = 3 (I is repeated three times to represent the number 3).
- Subtraction rule: Roman Numerals use subtraction when a smaller numeral precedes a larger one. For example, IX = X - I = 10 - 1 = 9.
- Limitation rule: This rule states that certain symbols like V, L, and D cannot be repeated. For example, 10 is written as X, not VV.



Hiralee Lalitkumar Makwana
About the Author
Hiralee Lalitkumar Makwana has almost two years of teaching experience. She is a number ninja as she loves numbers. Her interest in numbers can be seen in the way she cracks math puzzles and hidden patterns.
Fun Fact
: She loves to read number jokes and games.

















