In the realm of education and learning, the ability to comprehend and retain vast amounts of information is a crucial skill. With the ever-increasing complexity of subjects and the need for effective study techniques, learners are constantly seeking innovative methods to enhance their understanding and memory retention. One such technique that has gained widespread recognition and popularity is mind mapping for kids.
Originating from the field of cognitive psychology, mind mapping has emerged as a powerful study technique that promotes active learning, enhances creativity, and improves overall comprehension.
By visually organizing information in a non-linear and interconnected manner, mind mapping for kids stimulates the brain’s natural capacity for associative thinking, enabling learners to unlock their full potential and achieve remarkable results.
In this article, we will explore the concept of mind mapping, its principles, and its benefits as a powerful study technique that can revolutionize the way we learn and retain knowledge.
Table of contents
Benefits of Mind Mapping for Studying
When it comes to studying, we often find ourselves overwhelmed by copious amounts of information, complex concepts, and the daunting task of organizing it all. In such situations, mind mapping emerges as a powerful tool that can revolutionize the way we approach learning. Mind mapping for kids is a visual technique that helps us to generate, organize, and connect ideas in a meaningful and efficient manner. In this blog, we will explore the numerous benefits of mind mapping for studying and how it can enhance your learning experience. Utilizing mind mapping for kids offers a visual and structured approach, enhancing comprehension, organization, and retention of information.
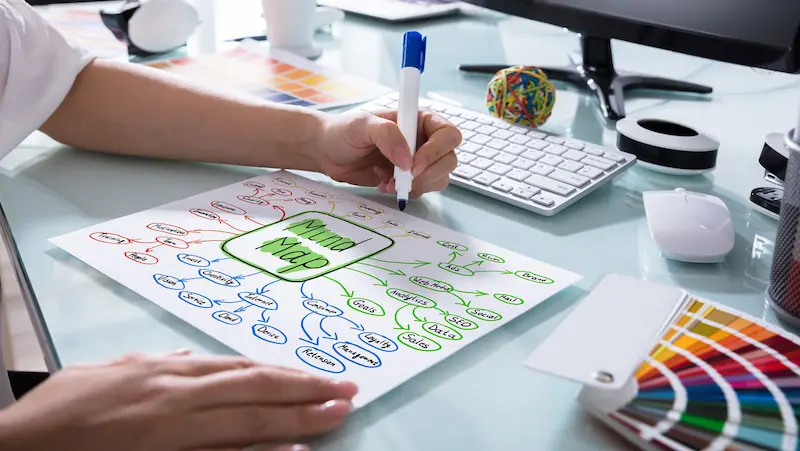

Enhanced Learning and Retention:
Mind mapping engages both sides of the brain, making it an effective tool for learning and retention. By visually representing information and creating associations between ideas, mind mapping taps into our natural thought processes, leading to improved understanding and memory recall.
The combination of images, colors, and keywords used in mind maps stimulates our creativity and aids in forming strong mental connections, making it easier to recall information during exams or when needed.
Improved Organization and Structure:
One of the significant challenges students face is organizing vast amounts of information into a coherent structure. Mind mapping allows you to break down complex subjects into manageable components, arranging them in a hierarchical and interconnected manner.
By creating a visual overview of the topic, mind maps provide a clear and logical structure, allowing you to see the big picture and understand how individual concepts relate to one another. This hierarchical organization not only facilitates comprehension but also enables you to identify any knowledge gaps that need further attention.
Boosted Creativity and Critical Thinking:
Mind mapping for kids encourages a free flow of ideas and promotes creative thinking. By using colors, drawings, and symbols, you can express your thoughts in a non-linear and imaginative way. This approach helps to unlock your creative potential, enabling you to generate unique connections and insights. Engaging children in a variety of kids activities encourages critical thinking, enabling them to analyze, problem-solve, and develop valuable cognitive skills.
Mind mapping also fosters critical thinking as you analyze information, make connections, and evaluate relationships between concepts. By engaging in active learning through mind mapping, you become an active participant in the learning process rather than a passive recipient of information.
Efficient Time Management:
With the abundance of information available, time management becomes crucial for students. Mind mapping allows you to organize your study sessions more effectively. By breaking down complex topics into smaller subtopics and prioritizing them, you can allocate time based on their importance and difficulty level.
Mind maps also serve as visual reminders of your progress, helping you track your learning journey. By utilizing mind maps, you can optimize your study time, focus on key concepts, and avoid getting overwhelmed by irrelevant details. Implementing a chore chart for kids instills responsibility and effective time management skills from a young age.
Enhanced Note-Taking and Reviewing:
Traditional linear note-taking can be tedious and limiting. Mind mapping, on the other hand, provides a more flexible and dynamic alternative. By using keywords, short phrases, and visual cues, mind maps enable you to capture essential information succinctly and in an organized manner.
During revision, mind maps serve as a condensed summary of the topic, making it easier to review and reinforce your understanding. Additionally, mind maps are highly customizable, allowing you to add new information or make connections as your knowledge deepens over time.
If you would like to know more about python for kids. Learn here!
Getting Started with Mind Mapping
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Basic Mind Map:
Step 1: Choose a Central Idea
Start by identifying the central idea or main topic you want to explore. This will be the core of your mind map, and all other ideas will radiate from it.
Step 2: Gather Your Materials
Before you begin, gather the necessary materials. You’ll need a large sheet of paper, a whiteboard, or a mind mapping software tool. If you prefer the traditional approach, colored pens, markers, and sticky notes will add a vibrant touch to your mind map.
Step 3: Draw the Central Node
Place the central idea at the center of your canvas and draw a circle or any other shape around it. This represents the starting point of your mind map.
Step 4: Branch Out
Next, start brainstorming related ideas or sub-topics that connect to the central node. Draw lines or branches radiating from the central node, each representing a different sub-topic. Use a unique color for each branch to distinguish between them.
Step 5: Add Secondary Nodes
From each sub-topic, continue branching out by adding secondary nodes. These nodes should contain more specific information or ideas related to the corresponding sub-topic. You can use keywords, images, or brief phrases to represent these ideas.
Step 6: Connect and Organize
As you continue expanding your mind map, look for connections between different nodes. Use lines or arrows to link related ideas, emphasizing relationships and creating a clear flow of information.
Step 7: Review and Refine
Take a step back and review your mind map. Ensure that the structure makes sense and that all the ideas are well-organized. Make adjustments as needed to improve clarity and coherence.
Tips for Selecting the Right Materials and Tools:
Digital vs. Analog: Choose the medium that suits your preferences and needs. Digital mind mapping tools offer the advantage of easy editing and cloud-based accessibility, while traditional pen-and-paper methods provide a tangible and tactile experience.
Mind Mapping Software: If you opt for digital mind mapping, explore various software options available. Popular choices include MindMeister, XMind, and SimpleMind. Look for user-friendly interfaces and features that cater to your specific requirements.
Colors and Symbols: Incorporate a color-coded system in your mind map to differentiate between topics and enhance visual memory. Additionally, use symbols and icons to represent ideas creatively.
Sticky Notes: For an interactive approach, use sticky notes on a whiteboard or large surface. This allows for easy repositioning and rearranging of ideas during brainstorming sessions.
Mind Mapping Apps: If you prefer convenience on the go, consider using mind mapping apps on your smartphone or tablet. These apps offer portability and the ability to capture ideas on the fly.
Know more about robotics kits for kids in this article.
Mind Mapping Techniques for Different Subjects
Mind mapping is a powerful technique that helps individuals visually organize their thoughts, ideas, and concepts. It is a versatile tool that can be applied to various subjects, enhancing learning and retention. Whether you’re studying math, science, languages, or history, mind mapping for kids can be an effective method to boost comprehension, creativity, and critical thinking. In this blog, we will explore specific ways in which mind mapping can be utilized for different subjects, enabling you to unlock your full learning potential. Introducing mind mapping for kids across different subjects can enhance their learning experience by visually organizing ideas and fostering a deeper understanding of various topics.

Mind Mapping for Math
Mathematics often involves complex concepts and interconnected ideas. Mind mapping can simplify the learning process by visually representing mathematical relationships and structures. Here are a few ways to use mind maps in math:
a. Formula visualization: Create a central node for a specific formula and branch out to represent different variables, equations, and their relationships. This visual representation aids in understanding and recalling formulas easily.
b. Problem-solving strategies: Use mind maps to outline step-by-step approaches to solving math problems. You can include relevant formulas, concepts, and examples to guide your problem-solving process effectively.
c. Concept mapping: Construct a mind map to interconnect various mathematical concepts, highlighting their dependencies and applications. This helps in understanding the broader context of mathematical ideas.
Mind Mapping for Science
Science encompasses various disciplines, including biology, chemistry, physics, and more. Mind mapping can be used as an effective study tool in science subjects. Here’s how:
a. Organizing scientific information: Mind maps can help you categorize and organize scientific facts, theories, and experiments. Use different branches to represent subtopics, and connect related ideas to establish meaningful connections.
b. Visualizing processes: Complex scientific processes, such as biological cycles or chemical reactions, can be easily visualized through mind maps. Use diagrams, symbols, and images to represent different stages and components of the process.
c. Cross-disciplinary connections: Science often involves interdisciplinary connections. Mind maps can assist in identifying and understanding the relationships between different scientific fields, promoting a holistic view of science.
Mind Mapping for Languages
Learning a new language involves memorizing vocabulary, understanding grammar rules, and practicing communication skills. Mind mapping can aid in language acquisition in the following ways:
a. Vocabulary building: Create a mind map to group related vocabulary words by themes or categories. Use images, associations, and example sentences to enhance memorization and recall.
b. Grammar visualization: Construct a mind map to visualize grammar rules, verb conjugations, sentence structures, and word relationships. This visual representation can make complex grammar concepts more accessible and memorable.
c. Conversation practice: Use mind maps to create dialogues and practice conversations. Branches can represent different speakers, and connecting lines can represent their responses, facilitating interactive language learning.
Mind Mapping for History
History involves understanding events, timelines, and cause-and-effect relationships. Mind mapping can help make historical information more engaging and interconnected:
a. Chronological organization: Construct a timeline-based mind map to visualize historical events in chronological order. Include key dates, names, and important details to understand the sequence of events better.
b. Cause-and-effect analysis: Use mind maps to explore the causes and effects of historical events. Branches can represent different causes and effects, allowing you to analyze and understand the relationships between them.
c. Historical figures and movements: Create mind maps to explore the contributions and characteristics of significant historical figures and movements. Branch out to represent their key accomplishments, philosophies, and connections with other figures or movements.
Integrating Mind Mapping into Study Routines

What is Mind Mapping?
Mind mapping for kids is a visual technique that helps us organize and represent information in a non-linear, creative way. It involves using diagrams, keywords, colors, and connections to capture and organize ideas. At its core, mind mapping for kids mirrors the way our brains naturally process and associate information, making it an effective tool for learning and studying.
Integrating Mind Mapping into Study Routines:
Preparing for Study Sessions:
Before diving into a study session, spend a few minutes creating a mind map to outline the main topics or concepts you will be covering. Start with a central topic or question and branch out into subtopics. This visual overview will provide you with a clear roadmap of what to expect, helping you stay focused and organized.
Note-taking and Reviewing:
During lectures or while reading textbooks, use mind maps to take notes. Instead of simply transcribing information, focus on capturing the main ideas and their relationships. Visual elements like colors, icons, and images can be used to enhance your understanding and create memorable associations. When reviewing your notes later, the mind map will serve as a concise and comprehensive summary.
Connecting Ideas:
One of the greatest benefits of mind mapping is its ability to facilitate connections between different ideas and concepts. Use the branches and connections in your mind map to identify relationships, draw parallels, and identify patterns. This approach encourages critical thinking and a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Problem Solving and Creativity:
Mind mapping for kids encourages a creative and free-flowing thought process. When faced with complex problems or essay writing, start with a central idea and brainstorm different solutions or arguments. The visual structure of a mind map allows you to generate ideas, explore various perspectives, and uncover hidden connections. This method can lead to innovative insights and more well-rounded arguments.
Exam Preparation:
As exams approach, mind maps become an invaluable tool for revision. Condense your notes into mind maps that highlight key concepts, relationships, and supporting details. The visual representation will make it easier to recall information during the exam and aid in structuring your responses.
Benefits of Mind Mapping in Study Routines:
Enhanced Creativity: Mind mapping stimulates both the analytical and creative parts of our brain, encouraging a more holistic approach to learning.
Improved Retention: The visual nature of mind maps engages our visual memory, making information more memorable and easier to recall.
Organized Thinking: Mind maps provide a structured framework for organizing thoughts, making complex subjects more approachable and manageable.
Efficient Study: By condensing the information into concise and visually appealing maps, you can save time and avoid information overload.
Enhanced Comprehension: Mind maps encourage a deeper understanding of concepts by highlighting connections and relationships, fostering a more comprehensive grasp of the subject matter.
Mind Mapping Tools and Resources
In today’s fast-paced digital era, traditional methods of learning and organizing information are being revolutionized by innovative digital tools. One such tool is mind mapping, a technique that aids in visualizing thoughts, connecting ideas, and enhancing creativity.
Mind mapping tools offer an engaging and interactive way for children to express their ideas, strengthen critical thinking skills, and improve organizational abilities. In this blog post, we will explore the world of digital mind mapping tools and introduce some excellent options suitable for children.
MindMeister:
MindMeister is a widely acclaimed mind mapping tool that is user-friendly and suitable for children of all ages. It provides an intuitive interface that allows kids to brainstorm, plan projects, and organize their thoughts. With its colorful and visually appealing design, MindMeister encourages creativity and collaboration. The tool also enables students to share their mind maps with teachers and peers, fostering a sense of teamwork and knowledge sharing.
Coggle:
Coggle is another popular digital mind mapping tool that offers a simplified approach for children to organize their ideas. It features a drag-and-drop interface that makes it easy for young users to create, edit, and collaborate on mind maps. Coggle allows children to express their thoughts visually using shapes, colors, and icons. With real-time collaboration features, children can work together on projects and share their maps with friends and family.
iMindMap Kids:
iMindMap Kids is specifically designed for younger children and provides a fun and interactive way to develop their creative thinking and organization skills. This tool uses vibrant visuals, playful animations, and sound effects to engage children in the mind mapping process. iMindMap Kids incorporates gamification elements to make learning enjoyable and offers a variety of templates and images tailored to children’s interests and age groups.
Popplet:
Popplet is a simple and user-friendly mind mapping tool suitable for younger children. It allows them to capture and organize their ideas in a visual manner, using colors, images, and text. With its intuitive interface, Popplet encourages children to create connections between ideas, helping them to understand relationships and develop critical thinking abilities. The tool also facilitates easy sharing and collaboration, making it ideal for classroom projects.
Mindomo:
Mindomo is a versatile mind mapping tool suitable for both children and teenagers. It offers a range of features, including colorful templates, multimedia integration, and real-time collaboration. Mindomo allows children to create dynamic mind maps that incorporate images, videos, and audio recordings, providing a multisensory learning experience. The tool supports project planning, note-taking, and brainstorming, making it a valuable asset for young learners.
Overcoming Challenges and Common Mistakes
Mind mapping for kids is a powerful tool that promotes creativity, critical thinking, and effective learning. It allows children to visually organize their thoughts, connect ideas, and gain a deeper understanding of various subjects. However, like any skill, using mind maps can present challenges for children. When considering child development and the use of mind mapping, it’s important to be aware of common mistakes that can hinder effective learning and cognitive growth.
In this blog post, we will explore some common obstacles young learners may encounter when using mind maps and provide strategies to help them overcome these challenges.

Difficulty in Generating Ideas:
One common challenge children face is generating ideas to populate their mind maps. Encourage them to start with a central topic or concept and brainstorm associated ideas. Engage them in discussions, ask open-ended questions, and provide prompts to stimulate their thinking. Remind them that there are no wrong answers during the brainstorming phase, as this will foster a sense of creativity and exploration.
Limited Organization and Structure:
Children may struggle with organizing their thoughts effectively on a mind map. Help them understand the importance of hierarchy and structure in mind mapping for kids. Teach them to use different branches or nodes to represent main ideas, subtopics, and supporting details. Encourage the use of colors, symbols, and images to visually enhance their maps and make them more engaging.
Lack of Flexibility and Adaptability:
Children might become fixated on a particular structure or pattern and find it challenging to modify or rearrange their mind maps. Teach them that mind maps are dynamic and flexible tools that can evolve as their understanding deepens. Encourage them to revise and reorganize their maps whenever necessary, emphasizing the benefits of adaptability in enhancing clarity and coherence.
Limited Use of Keywords and Abbreviations:
Children may struggle to condense their ideas into concise keywords or abbreviations. Help them develop the skill of summarizing concepts by highlighting keywords or using abbreviations to represent longer phrases. Provide examples and practice exercises to improve their ability to capture essential information succinctly. This will enhance their map’s readability and make it easier for them to recall information.
Fear of Making Mistakes:
Children often fear making mistakes or creating “messy” mind maps, which can hinder their creativity and exploration. Emphasize the importance of embracing mistakes as valuable learning opportunities. Encourage them to experiment, take risks, and learn from any perceived errors. Remind them that mind maps are personal tools for organizing thoughts, and there is no right or wrong way to create them. Teaching emotional regulation for kids, including addressing their fear of making mistakes, can be supported through techniques like mind mapping, fostering resilience and self-confidence.
Lack of Practice and Review:
Using mind maps effectively requires practice and regular review. Help children develop a habit of using mind maps consistently across different subjects and activities. Encourage them to review and revise their maps periodically to reinforce their learning. As they become more familiar with mind mapping for kids, it will become a natural and effective tool for organizing their thoughts and ideas.
Conclusion
Mind mapping for kids offers a practical and engaging approach to organizing information, enhancing memory retention, and fostering creative thinking. By encouraging their children to use mind maps, parents can help them develop critical thinking skills, improve their learning experience, and achieve better academic outcomes.
By engaging in open communication with their children, parents can understand their unique learning styles, strengths, and weaknesses. This knowledge will enable them to provide tailored guidance and support, incorporating mind mapping for kids techniques into their children’s study routines.
Parents can help their children identify key concepts, break down complex topics, and establish meaningful connections between ideas using mind maps. They can also assist in setting goals, creating study schedules, and reinforcing time management skills, ensuring that their children have a well-structured approach to their studies.
In conclusion, by actively engaging in their children’s education, understanding their individual needs, and promoting the use of mind mapping, parents can significantly contribute to their children’s academic success. Learn about coding camps for kids near me also.
BrightChamps offers the best coding for kids, providing a comprehensive and engaging platform for young learners to explore the world of programming.
Exploring the diverse educational offerings on BrightChamps opens up exciting opportunities for children to learn and thrive in a supportive and dynamic online environment.
BrightChamps blog page offers valuable insights, tips, and resources to support children’s education and holistic development.
Frequently Asked Questions
A1. Mind mapping is a visual technique that organizes information around a central concept, helping to connect and recall ideas more effectively.
Mind mapping enhances study habits by improving memory retention, aiding in information organization, and promoting creative thinking.
A2. Mind mapping promotes effective learning by engaging both hemispheres of the brain, facilitating connections between concepts, and enhancing memory retention through visual and spatial representation.
A3. Key benefits of mind-mapping techniques include improved understanding of complex topics, enhanced creativity, better organization of information, and increased retention and recall.
A4. Mind mapping helps improve organization and time management skills by providing a visual overview of the study material, allowing students to prioritize tasks, identify key areas, and create structured study plans.
A5. Mind mapping is effective for studying various subjects and topics, including but not limited to literature, science, history, mathematics, and languages. Its flexibility makes it applicable across different disciplines.
A6. a. Start with a central topic or concept in the center of the page.
b. Use colors, images, and keywords to represent different ideas.
c. Connect related ideas with lines and branches.
d. Keep the structure organized and hierarchical.
e. Review and revise the mind map regularly to reinforce learning.
A7. Yes, there are various digital mind mapping tools available, such as MindMeister, XMind, and Coggle, which provide user-friendly interfaces, collaboration features, and the ability to create visually appealing mind maps.
A8. Mind mapping adds an element of creativity and interactivity to studying, making it more engaging and enjoyable for children. They can use colors, images, and personal associations to make the mind maps visually appealing and memorable.
A9.Yes, several studies have shown that mind mapping improves learning and retention. Research indicates that mind mapping stimulates the brain’s associative thinking and enhances memory consolidation, leading to better academic performance.
A10. While specific testimonials may vary, many students have reported improved comprehension, better organization, and increased confidence in exams after adopting mind-mapping techniques. Mind maps have helped them break down complex information and retain it more effectively.

 We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.
We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.