Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, affecting various aspects of daily life. Parental support is crucial in managing ADHD, providing emotional understanding, advocating for educational needs, and implementing consistent strategies at home. A supportive environment fosters resilience, enabling children with ADHD to navigate challenges more effectively.
In this blog, discover effective strategies for ADHD support, including personalized routines to enhance focus and communication techniques fostering positive interactions. Explore practical tips aimed at creating a supportive environment that empowers individuals with ADHD to thrive in various aspects of life.
Table of contents
Understanding ADHD
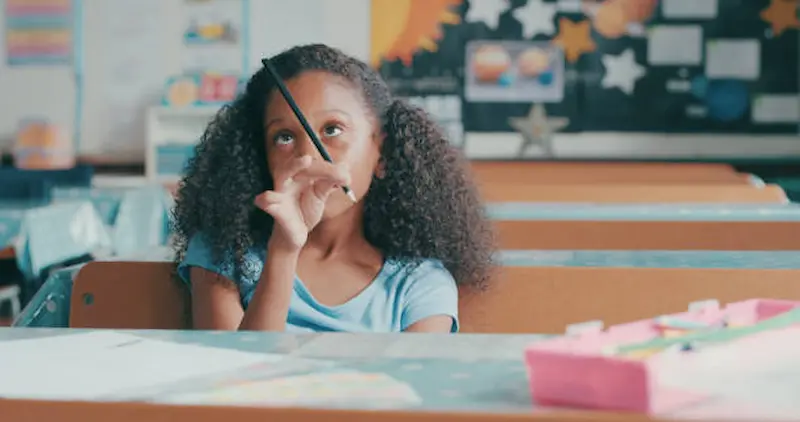

A. What is ADHD?
Types of ADHD
- Inattentive: Characterized by difficulty sustaining attention, often leading to careless mistakes in tasks.
- Hyperactive: Manifests as excessive movement, restlessness, and impulsive behavior.
- Combined: A blend of inattentive and hyperactive traits, creating a more complex presentation.
Common Symptoms and Behaviors
- Inattention may lead to forgetfulness, easily distracted, and challenges in organizing tasks.
- Hyperactivity involves constant fidgeting, difficulty staying seated, and impulsive decision-making.
- Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention and effective management.
B. Causes and Risk Factors
- Genetic predisposition plays a significant role, with ADHD often running in families.
- Variances in brain structure and function, particularly related to neurotransmitter activity.
- Environmental factors such as prenatal exposure to tobacco or lead may contribute.
C. Diagnosis and Assessment
- Role of Healthcare Professionals
- Psychiatrists, psychologists, and pediatricians collaborate for a holistic diagnosis.
- Comprehensive evaluation includes interviews, observations, and input from parents, teachers, and caregivers.
- Assessing Your Child’s Symptoms
- Regularly track behaviour patterns, noting specific situations triggering symptoms.
- Share detailed observations with healthcare professionals for a comprehensive understanding.
- Collaborate on a personalised intervention plan, incorporating behavioural strategies, therapy, and, if necessary, medication for optimal management. Early diagnosis and a tailored approach significantly improve outcomes for individuals with ADHD.
The Impact of ADHD on Children
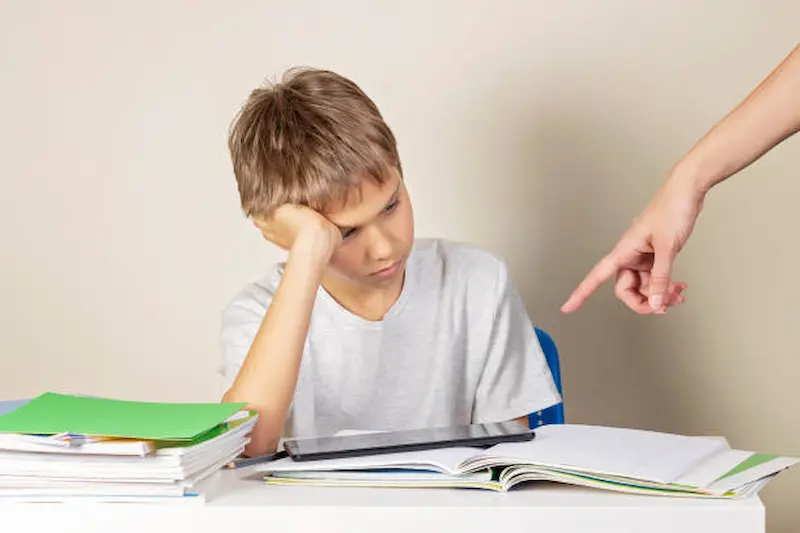

A. Academic Challenges
How ADHD Affects School Performance: ADHD can significantly impact academic performance, with challenges in focus, organization, and completing tasks. Recognizing these difficulties early allows for tailored support and intervention strategies. Implementing targeted activities for kids, such as interactive and structured learning exercises, can play a crucial role in addressing these challenges.
Recognizing Learning Disabilities: ADHD often coexists with learning disabilities. Identifying specific challenges, such as dyslexia or dyscalculia, ensures a comprehensive approach to addressing academic hurdles and providing the necessary resources.
Accessing targeted learning resources tailored to individual needs becomes crucial in supporting children facing these dual challenges.
B. Social and Emotional Effects
Building Self-esteem: Children with ADHD may face self-esteem challenges due to academic struggles. Fostering a supportive environment, acknowledging achievements, and emphasizing strengths contribute to building confidence.
Managing Frustration and Anxiety: Teaching coping mechanisms helps children manage frustration and anxiety associated with ADHD. Social skills training and emotional support are vital components in fostering resilience and positive emotional well-being.
Building a Supportive Environment
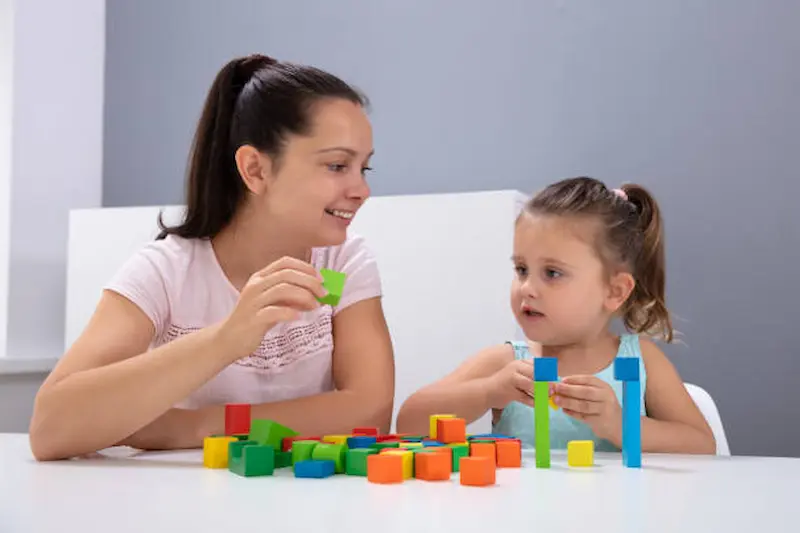

A. Parental Involvement
Actively participating in a child’s life fosters a strong support system. Positive parenting practices, such as engaging in their interests, attending school events, and maintaining open lines of communication, play a crucial role in building a healthy parent-child relationship.
Open communication allows for a better understanding of the child’s needs and challenges, facilitating a collaborative approach to support.
B. Creating a Structured Routine
Establishing daily schedules and timetables provides stability, helping children with ADHD navigate tasks effectively.
Consistency in routine is crucial, offering predictability that aids in managing ADHD symptoms and promoting a supportive environment.
Positive Reinforcement and Discipline

A. Behavioral Strategies
- Rewards and Consequences: Implement a system of positive reinforcement for desired behaviors and appropriate consequences for undesired actions. This helps children understand the link between behavior and outcomes.
- Setting Clear Expectations: Clearly communicate expectations, allowing children to comprehend the boundaries and standards, fostering a sense of structure and predictability. Instilling good habits for kids, such as regular routines, responsibility for personal belongings, and time management, further reinforces these expectations.
B. Effective Discipline Techniques
- Time-outs and Grounding: Employing time-outs and grounding can be effective consequences, providing children with an opportunity to reflect on their actions and learn from mistakes.
- Avoiding Punitive Measures: Strive for discipline approaches that focus on teaching rather than punishment, fostering a positive and supportive environment for children’s emotional and behavioral development.
Encouraging Healthy Habits

A. Nutrition and ADHD
The Role of Diet in Symptom Management: While no specific ADHD diet exists, a balanced and nutrient-rich diet can positively influence symptom management. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, may offer cognitive benefits.
Foods to Include and Avoid: Prioritize whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Limiting processed foods, artificial additives, and excessive sugars can contribute to a more stable energy level and attention span.
B. Promoting Physical Activity
Exercise and Its Impact on Focus: Regular physical activity has been linked to improved focus and cognitive function, making it a beneficial component of ADHD management.
Encouraging Sports and Activities: Engaging children in sports and activities not only supports physical health but also provides opportunities for structured routines and social interaction, contributing to overall well-being and positive ADHD symptom management. Incorporating fun games for kids into these activities adds an extra layer of enjoyment, making the experience more engaging and reinforcing the benefits of regular physical and social engagement.
Medication Management

A. Medication Options for ADHD
- Stimulants and Non-Stimulants: Stimulant medications, like methylphenidate and amphetamines, and non-stimulant options, such as atomoxetine, provide diverse choices for managing ADHD symptoms, each with distinct mechanisms.
- Understanding the Pros and Cons: While medications can effectively alleviate symptoms, understanding potential benefits and drawbacks is crucial. Monitoring individual responses aids in tailoring the approach to the specific needs of the individual.
B. Working with Healthcare Professionals
- Monitoring and Adjusting Medication: Regular communication with healthcare providers is essential for monitoring medication efficacy and making necessary adjustments to dosage or type.
- Handling Side Effects: Collaborating with professionals helps address and manage potential side effects, ensuring a balanced and effective treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs. Regular check-ins contribute to optimal medication management for ADHD.
Special Education Services

A. Individualized Education Plans (IEPs)
Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) are tailored strategies for students with ADHD, outlining personalized goals, accommodations, and support services to ensure academic success. Collaborative efforts involving educators, parents, and specialists contribute to the development and implementation of effective IEPs.
B. 504 Plans and Accommodations
504 Plans provide accommodations for students with ADHD to create an inclusive learning environment.
These may include extended test-taking time, preferential seating, or additional breaks, accommodating the unique needs of each student for an equitable educational experience.
C. Advocating for Your Child’s Educational Needs
Parents play a vital role in advocating for their child’s educational needs, ensuring open communication with educators, participating in IEP or 504 Plan meetings, and staying informed about available resources to create a supportive educational journey for children with ADHD.
Support Systems for Parents

A. Parenting Support Groups
Engaging in parenting support groups provides a valuable platform for sharing experiences, gaining insights, and building a network of understanding individuals. This exchange of parenting advice and collective wisdom enhances the overall support system. Connecting with others facing similar challenges fosters a sense of community and emotional support.
B. Professional Counseling and Therapy
Seeking professional counseling and therapy offers parents a structured space to address the emotional impact of raising a child with ADHD.
Therapists provide coping strategies, effective communication tools, and a supportive environment for emotional well-being.
C. Stress Management Techniques
Implementing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, exercise, and time management, empowers parents to navigate challenges effectively. This proactive approach not only benefits parents but also creates a conducive environment for fostering stress management for kids, particularly those dealing with conditions like ADHD. Prioritizing self-care contributes to resilience, ensuring parents can model and provide the necessary support for their child with ADHD, helping them develop valuable coping skills from an early age.
Conclusion
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, while presenting challenges, often comes with unique strengths. Individuals with ADHD may exhibit heightened creativity, innovation, and adaptability, showcasing that neurodiversity can bring valuable perspectives and contributions to various aspects of life and work. Embracing and harnessing these benefits can lead to a more inclusive and enriched understanding of cognitive diversity.
Elevate your child’s learning journey with BrightChamps, the leading EdTech company offering a transformative blend of robotics, financial education, and coding courses.
To get your hands on more such articles, educational content, and free resources on coding for kids, robotics courses, game development, etc., check out the BrightCHAMPS Blog Page now!
Frequently Asked Questions ( FAQs )
A1. The main symptoms of ADHD in children include inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, and difficulty organizing tasks.
Q2. How is ADHD diagnosed in children?
A2. ADHD in children is diagnosed through a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals, involving interviews, observations, and input from parents, teachers, and caregivers.
Q3. Are there natural remedies for managing ADHD symptoms?
A3. While there are no proven natural remedies for ADHD, some find benefits in dietary adjustments, regular exercise, and mindfulness practices.
Q4. What role do teachers play in supporting children with ADHD?
A4. Teachers play a crucial role in supporting children with ADHD by implementing tailored teaching strategies, providing structure, and collaborating with parents and specialists.
Q5. Can ADHD be outgrown, or is it a lifelong condition?
A5. ADHD is typically a lifelong condition, but with proper management, individuals can learn to cope effectively, and symptoms may evolve over time.
Q6. How can I help my child with ADHD succeed academically?
A6. Supporting academic success in children with ADHD involves creating a structured environment, utilizing effective study habits, and collaborating with teachers for individualized support.


 We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.
We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.