Understanding the developmental milestones for infants is crucial for parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals as these milestones encompass a wide range of skills and abilities that infants acquire as they grow and develop. They serve as benchmarks for typical development, allowing for tracking of an infant’s progress and early identification of any potential delays or concerns.
By actively engaging with their child’s development and providing appropriate support, parents can create a nurturing environment that stimulates growth in areas such as motor skills, cognitive abilities, social and emotional development, and language and communication skills. Recognizing and celebrating these milestones not only supports an infant’s development but also strengthens the parent-child bond. Overall, understanding and monitoring developmental milestones are essential for promoting an infant’s overall growth and well-being.
Table of contents
Understanding Developmental Milestones
What are developmental milestones?
Developmental milestones for infants are key skills or abilities that infants acquire as they grow and develop. These milestones cover various areas of development, including physical, cognitive, social, emotional, and language skills. They serve as benchmarks for typical development and help track a child’s progress during the infant stage.
Why are developmental milestones important?
Developmental milestones for infants are important because they provide a framework for assessing a child’s growth and development during this critical period. They help parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals monitor an infant’s progress and identify any potential developmental delays or concerns. Early detection and intervention can greatly benefit an infant’s overall development and well-being.
Understanding and observing important milestones for infants enable parents to actively engage with their child’s development. By recognizing and supporting these milestones, parents can provide age-appropriate activities and create a nurturing environment that stimulates their infant’s growth in various domains. Celebrating and encouraging the achievement of milestones not only supports the infant’s development but also strengthens the bond between the parent and child.
Motor Development Milestones
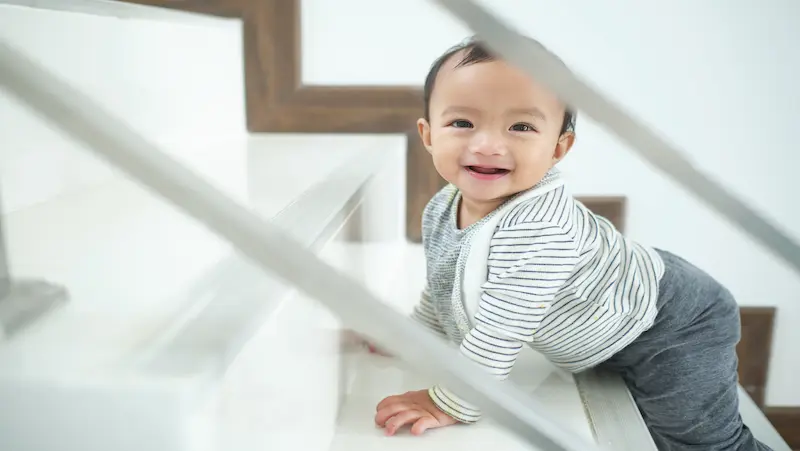

Gross Motor Skills
1.Rolling Over: Rolling over is an important gross motor skill that infants typically develop around 3 to 6 months of age. Initially, they learn to roll from their stomach to their back and later progress to rolling from their back to their stomach. This skill strengthens their core muscles, enhances coordination, and allows them to explore their surroundings independently.
2.Sitting Up: Sitting up without support is a significant milestone in gross motor development, usually achieved around 6 to 8 months of age. Infants gradually gain control over their head, neck, and trunk muscles, enabling them to sit upright without toppling over. This skill not only provides stability for engaging in play and exploration but also lays the foundation for further motor development, such as crawling and walking.
3.Crawling: Crawling is a fundamental gross motor skill that infants typically acquire around 6 to 10 months of age. It involves coordinating their arms and legs to move their body across the floor. Crawling promotes strength and coordination in the upper body, enhances spatial awareness, and prepares infants for more complex locomotor skills.
4.Pulling Themselves Up to Stand: Around 8 to 12 months of age, infants begin to develop the strength and coordination to pull themselves up to a standing position using furniture or other objects for support. This skill strengthens their leg muscles, improves balance, and sets the stage for further exploration and mobility, such as cruising and walking.
5.Walking: Walking independently is a major milestone in gross motor development, typically achieved between 9 to 15 months of age. Infants progressively gain stability and coordination in their legs and gradually transition from holding onto objects for support to taking their first steps. Walking allows infants to explore their environment, enhances their mobility, and opens up a world of new experiences.
Fine Motor Skills
1.Grasping objects: Infants initially use a reflexive grasp, but as they grow, they develop the ability to purposefully reach for and hold objects. In the early months, infants explore objects by swiping at them or using a palmar grasp, where they close their entire hand around the object. As their fine motor skills develop, they progress to a more refined grasp, using their fingers to pick up and manipulate objects. This milestone is crucial for their ability to interact with and explore their environment.
2.Pincer grasp: Around 8 to 12 months, infants begin to develop the pincer grasp, which involves using the thumb and index finger to pick up small items. Initially, they may use a crude version of the pincer grasp by using the palm and side of the fingers. However, with practice and increased coordination, they refine their skills and develop the ability to pick up small objects between their thumb and index finger with precision. This milestone enables infants to engage in activities such as feeding themselves finger foods, stacking blocks, and manipulating small objects.
Robotics for kids online provides an engaging and educational platform where young learners can explore the exciting world of technology and programming.
3.Scribbling or drawing: As infants’ hand-eye coordination improves, they start to make intentional marks with crayons, markers, or other drawing tools. Initially, their scribbles may be random, but over time, they gain better control and produce more purposeful lines and shapes. Scribbling and drawing are not only creative outlets for infants but also help in refining their fine motor skills. It requires coordination between the eyes, hands, and fingers to control the movements and create specific shapes or lines.
Cognitive Development Milestones
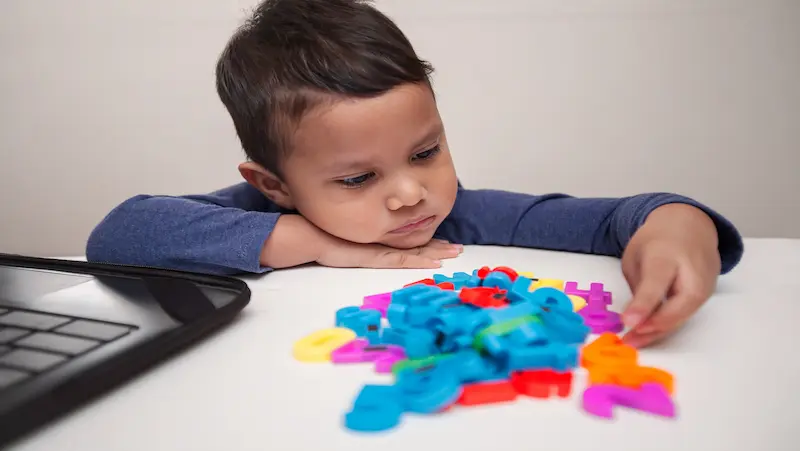

Cognitive Skills
1.Object Permanence: Object permanence is the understanding that objects continue to exist even when they are out of sight. Infants initially lack this understanding but gradually develop it around 8 to 12 months of age. They begin to realise that objects exist even when they are hidden or removed from their view. This skill is essential for memory development and lays the foundation for more complex cognitive abilities.
2.Cause and Effect: Infants gradually learn to understand cause and effect relationships. They begin to realise that their actions can produce specific outcomes. For example, they may learn that pressing a button on a toy causes it to light up or produce a sound. This understanding helps infants make sense of the world around them and is an important cognitive skill for problem-solving and learning.
3.Spatial Awareness: Spatial awareness refers to the ability to understand and perceive the spatial relationships between objects and oneself. Infants start to develop spatial awareness as they explore their environment. They learn to navigate through spaces, reach for objects accurately, and understand concepts like “in,” “on,” and “under.” This skill is crucial for spatial reasoning, visual perception, and later mathematical understanding.
4.Memory: Infants demonstrate early memory capabilities, including recognition memory and recall memory. They can remember familiar faces, objects, and events. As they grow, their memory capacity expands, allowing them to remember past experiences and build on their knowledge. Memory plays a significant role in learning, language development, and problem-solving.
5.Symbolic Play: Symbolic play involves using objects or actions to represent something else. Infants engage in early forms of symbolic play as they pretend with objects, such as using a block as a phone. This type of play demonstrates their ability to use symbols and imagination, fostering creativity, cognitive flexibility, and abstract thinking.
Social and Emotional Development Milestones
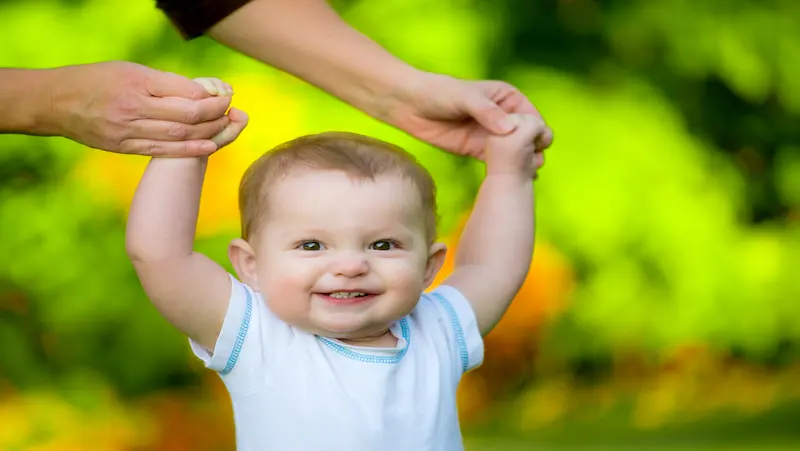

Social Development
Social development milestones in infants involve their ability to interact with others and understand social norms. These milestones play a crucial role in their social-emotional growth. Infants achieve various social milestones such as smiling and cooing in response to others, making eye contact, engaging in turn-taking games, and showing interest in other children. As they progress, infants learn to play alongside peers, display empathy or concern for others, follow simple social rules, and initiate interactions with others. These milestones indicate their developing social skills, emotional understanding, and ability to engage with their social environment.
Nurturing these social milestones is important for infants’ social development. Creating supportive environments that encourage positive interactions, providing opportunities for play and socialization, and modeling appropriate social behaviors can help infants build strong social connections and develop healthy social skills. Supporting their social-emotional growth in the early years sets the foundation for positive social relationships and well-being as they continue to grow and interact with the world around them.
Emotional Development
Tracking milestones in infants is important for understanding their emotional development. Emotional milestones in infants encompass their ability to understand and regulate their emotions, contributing to their overall emotional well-being. Infants achieve various emotional milestones, such as expressing a range of emotions, developing a secure attachment to caregivers, and demonstrating self-soothing techniques. They also begin to show empathy towards others and develop coping strategies to manage stress.
Achieving milestones in infancy is a significant aspect of a child’s development. Supporting these emotional milestones is crucial for infants’ emotional well-being. By providing a nurturing and responsive caregiving environment, parents and caregivers can help infants develop healthy emotional skills. Encouraging emotional expression, fostering secure attachments, and teaching coping strategies contribute to their emotional development and lay the foundation for their future emotional growth and resilience. Tracking and celebrating these milestones allow parents and caregivers to actively engage in their infant’s emotional development and provide the necessary support and guidance to promote their emotional well-being.
Language and Communication Milestones

Language Skills
1.Babbling and Vocal Exploration: Infants reach language milestones by engaging in babbling and making various sounds as they explore their vocal abilities. This stage is crucial for developing the muscles involved in speech production and laying the foundation for future language development.
2.Comprehension and Name Recognition: As language skills progress, infants begin to respond to their name, indicating their growing language comprehension and recognition of their own identity. They start to understand simple words and commands, expanding their receptive language skills.
3.Gestures for Communication: Infants use gestures such as pointing and waving to communicate their needs and intentions before they develop verbal language skills. These gestures provide a bridge between non-verbal and verbal communication and facilitate early interactions with caregivers.
4.First Words and Phrase Formation: Language milestones include infants saying their first words and gradually combining words to form short phrases. This marks an important step in expressing their thoughts and desires and communicating with others.
5.Comprehension of Questions and Directions: As infants’ language comprehension grows, they develop the ability to understand simple questions and follow basic directions. This demonstrates their increasing understanding of language and their ability to engage in basic conversations.
Communication Skills
1.Eye Contact and Social Engagement: Communication milestones for infants include making eye contact during interactions, which establishes a foundation for social engagement and connection. It allows infants to establish a connection with others and communicate their presence and interest.
2.Gestures for Communication: Infants use gestures such as pointing or reaching to communicate their needs and desires, bridging the gap between non-verbal and verbal communication. These gestures serve as a way for infants to express their intentions and initiate interactions with others.
3.Back-and-Forth Babbling: Infants engage in back-and-forth babbling or conversations with caregivers, taking turns in vocalisations and imitating sounds. This early communication skill demonstrates their ability to engage in reciprocal interactions and lays the groundwork for future language development.
4.Responding to Questions and Requests: As infants’ communication skills progress, they begin to respond to simple questions or requests from caregivers, indicating their growing understanding and ability to engage in basic exchanges. This milestone shows their increasing comprehension and responsiveness in communication.
5.Initiating Communication and Conversational Skills: Infants start to initiate communication with others, using a variety of sounds and intonation patterns to convey their thoughts and intentions. They develop an understanding of non-verbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language, and incorporate them into their communication. Additionally, they begin to develop basic conversational skills, such as taking turns and staying on topic, enhancing their ability to engage in meaningful interactions.
Parents should encourage their children to learn coding for kids from an early age to foster creativity and problem-solving skills.
Conclusion
Developmental milestones are important markers of a child’s growth and progress. They encompass various areas of development, including motor skills, cognitive abilities, social interactions, emotional understanding, and language acquisition. By understanding and tracking these milestones, parents and caregivers can provide appropriate support and stimulation to foster their child’s development.
Also, BrightChamps provides a comprehensive platform for learning about money for kids, offering interactive and engaging resources that teach financial literacy, budgeting, saving, and other essential money management skills.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
A1: Developmental milestones for infants are key skills or abilities that infants acquire as they grow and develop. They are important for the wholesome generation of attributes and key values that a child can possess.
A2: Parents can track and monitor their infant’s developmental milestones by following available resources such as books or creating a stimulating environment at home that supports their child’s development.
A3: Motor milestones infants achieve in their first year include skills such as running, hopping, and jumping. These milestones indicate the development of their gross motor skills.
A4: Common communication and language milestones in infancy include understanding basic nouns and pronouns. These milestones represent the growing language comprehension and expression skills of infants.
A5: The cognitive milestones parents can expect to see as their baby grows involve skills such as thinking, learning, exploring, and problem-solving. These milestones reflect the development of the child’s brain and impact other areas of their development, including language and social skills.


 We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.
We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.