The Japanese education system has long been admired and studied worldwide for its remarkable achievements and unique approach to nurturing young minds. Its significance extends beyond borders, serving as a source of inspiration for educators, policymakers, and parents alike. In this brief exploration, we will delve into the key aspects that make the Japanese education system stand out and the valuable lessons it offers to the global community.
Table of contents
- Key Components of the Japanese Education System
- Teaching Methods and Philosophy
- Challenges in the Japanese Education System
- The Role of Technology in Education
- Cultural Influences on Education
- Preparing Students for the Future
- The Success of the Japanese Education System
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Key Components of the Japanese Education System
The Japanese education system is renowned for its rigor and effectiveness. It comprises various key components that shape the educational journey of students in Japan.
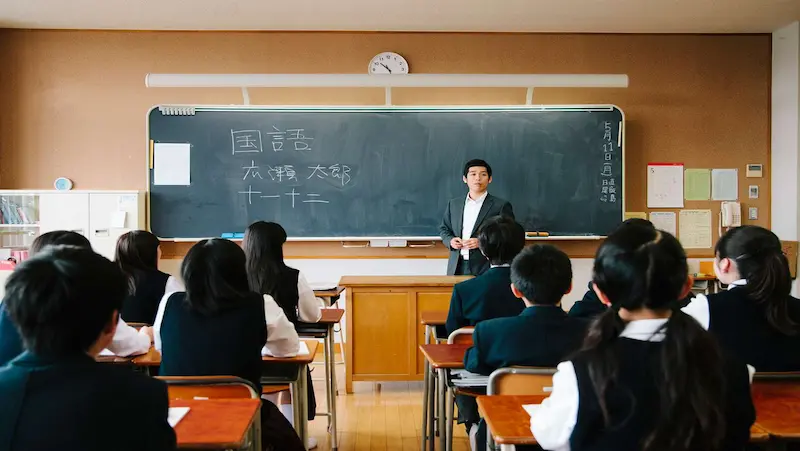

School Levels and Structure
1. Elementary Education: Elementary school in Japan typically spans six years, starting from age six. Students receive a broad education foundation, including subjects like math, Japanese language, science for kids, social studies, and physical education.
2. Junior High School: After completing elementary school, students move on to junior high school for three years. Here, they continue to study core subjects while also delving into practical life skills and moral education.
3. Senior High School: Senior high school education is divided into general and vocational tracks. The general track focuses on preparing students for university entrance exams, while the vocational track emphasizes practical skills and prepares students for immediate employment after graduation.
4. Higher Education: Higher education in Japan includes universities and colleges. Universities offer four-year bachelor’s degree programs, while colleges typically provide two-year associate degree programs or specialized vocational training.
Curriculum and Subjects
1. Core Subjects: Core subjects form the backbone of the Japanese curriculum. These include mathematics, Japanese language and literature, science, social studies, and physical education. Japanese students spend significant time mastering these subjects to build a strong academic foundation.
2. Specialized Tracks: In senior high school, students have the option to choose specialized tracks that align with their interests and career goals. These tracks include humanities, natural sciences, and vocational training. Humanities focus on subjects like literature and history, while natural sciences delve into fields like physics and chemistry.
Teaching Methods and Philosophy

Focus on Group Dynamics
Learning doesn’t happen in a vacuum; it thrives within the vibrant ecosystem of group dynamics. When students collaborate, share ideas, and work collectively towards a common goal, they not only gain academic knowledge but also develop essential life skills like communication, teamwork, and problem-solving. As teachers, fostering an inclusive and supportive classroom environment is key to nurturing these skills.
Emphasis on Moral Education
Education should extend beyond textbooks and exams. It should encompass the development of responsible and empathetic citizens. Moral education plays a pivotal role in shaping individuals who value ethics, compassion, and social responsibility. Encouraging discussions on ethical dilemmas, promoting empathy, and modeling virtuous behavior can all contribute to this aspect of education.
Role of Teachers
Teachers are the guiding lights in a student’s educational journey. Beyond delivering content, they serve as mentors, motivators, and role models. Their influence extends far beyond the classroom, shaping young minds and nurturing their potential. It’s the duty of teachers to inspire curiosity, instill a love for learning, and provide the support students need to flourish.
Innovative Teaching Techniques
Education should adapt to the times. Innovative teaching kids kindness techniques inject vitality into the learning process. Whether it’s using technology to enhance engagement or implementing interactive activities for kids that cater to various learning styles, these methods keep education relevant and captivating.
Challenges in the Japanese Education System

1. Pressure and Stress
Imagine being a high school student in Japan. You not only have to juggle textbooks and exams but also the weight of societal expectations. The relentless pressure to excel in academics and extracurricular kids activities often leads to sleepless nights and emotional turmoil. This intense pressure cooker environment can take a toll on the mental and emotional regualtion activities for kids well-being of young minds.
2. Gender Inequality
Japan, known for its cutting-edge technology and innovation, still grapples with gender disparity in its education system. Although strides have been made, girls often face societal biases and stereotypes, limiting their access to certain fields of study. Encouraging girls to pursue STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) subjects remains a challenge that the Japanese education system continues to address.
3. Pressure to Conform
The Japanese phrase “the nail that sticks out gets hammered down” encapsulates the struggle for individuality in the education system. Students are expected to conform to societal norms and expectations, often stifling their creativity and unique talents. This conformity can hinder personal growth mindset books for kids and hinder the development of critical thinking skills.
4. Teacher Shortages
Behind every successful education system are dedicated teachers. Unfortunately, Japan faces a significant shortage of educators, particularly in rural areas. Overworked teachers often grapple with large class sizes, making it challenging to provide individualized attention to each student. This issue not only affects the quality of education but also places additional stress management for kids on educators themselves.
The Role of Technology in Education
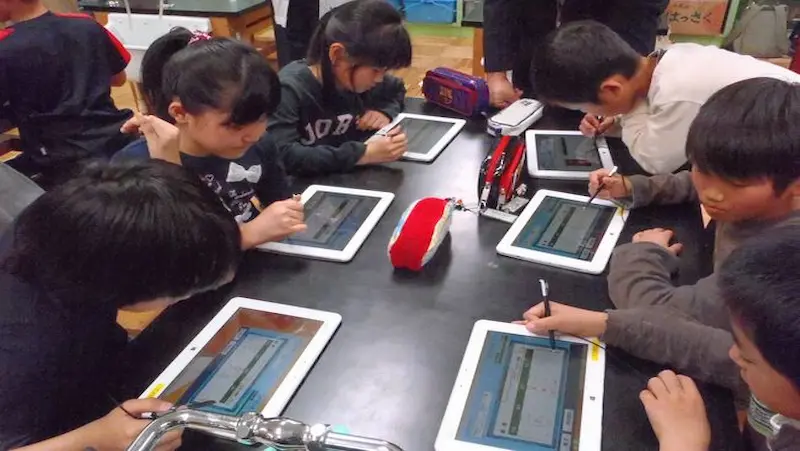

Integration of Technology
Gone are the days when classrooms were limited to chalkboards and textbooks. Technology has ushered in a new era of interactive learning games for kids. Smartboards, tablets, and educational software have made lessons more engaging and accessible. Teachers can customize content to cater to individual student needs, making education more personalized and effective.
Moreover, technology has bridged geographical barriers, connecting students and educators from around the globe. Virtual field trips, video conferences, and collaborative projects enable students to explore diverse perspectives and cultures. This integration of technology enhances the overall educational experience, preparing students for a digitally-driven world.
E-learning and Online Education
The internet has opened up a world of opportunities for learners of all ages. E-learning and online education have gained immense popularity, offering flexibility and convenience. Whether it’s pursuing a degree, learning a new skill, or simply accessing resources, the internet is a treasure trove of knowledge.
Online schooling platforms and courses provide learners with the freedom to set their own pace, accommodating busy schedules and diverse learning styles. This accessibility is particularly valuable for working professionals and those with limited access to traditional education.
Cultural Influences on Education

Confucian Values
Confucianism, with its deep-rooted principles of respect for authority, filial piety, and the pursuit of knowledge, has left an indelible mark on education in many East Asian countries. In Confucian-inspired societies like China and South Korea, students often approach education with a strong emphasis on discipline, memorization, and reverence for teachers. The Confucian heritage values education as the key to social harmony and personal development, shaping study habits and educational goals in these regions for centuries.
Traditional Japanese Values
In Japan, traditional values like “wa” (harmony) and “gaman” (perseverance) have deeply influenced their education system. Japanese students are encouraged to work together harmoniously and show resilience in the face of challenges. The concept of “ichi-go ichi-e” (treasure every encounter, for it will never recur) promotes a strong focus on the present moment in the classroom, fostering a deep connection between students and teachers. This traditional Japanese approach highlights the importance of holistic development, including moral and emotional growth.
Globalization and Cultural Shifts
In today’s interconnected world, the cultural influences on education are evolving rapidly. Globalization has brought diverse cultures and ideas into educational settings, creating a fusion of teaching kids responsibility methods, values, and perspectives. As a result, students are exposed to a broader range of worldviews and are encouraged to embrace cultural diversity. This shift towards multiculturalism fosters open-mindedness, empathy, and a broader understanding of the global community.
Preparing Students for the Future

Career Guidance and Counseling
One key aspect of preparing students for the future is providing them with effective career guidance and counseling. It’s about more than just helping them choose a job; it’s about helping them discover their passions and strengths. Students should be encouraged to explore different career paths, understand the demands of various professions, and set realistic goals. Career counselors play a vital role in this process, offering insights and advice that can shape a student’s future.
College Entrance Exams
For many students, college is a stepping stone to their desired careers. Therefore, college entrance exams are a crucial part of their journey. These exams, such as the SAT or ACT, assess a student’s readiness for higher education. To prepare, students can take practice tests, seek guidance from teachers and mentors, and work on strengthening their academic skills. Remember, these exams are not just about scores; they’re about gaining access to opportunities and pursuing one’s passions.
Preparing for a Globalized World
In today’s interconnected world, global awareness and adaptability are invaluable traits. Students should be exposed to diverse cultures and perspectives, fostering open-mindedness and empathy. Language skills and cross-cultural understanding can open doors to international opportunities. Encourage students to engage in cultural exchanges, study abroad programs, or even just learn a new language. These experiences will prepare them for success in a globalized society.
The Success of the Japanese Education System

Academic Achievements
One of the standout features of the Japanese education system is its focus on academic excellence. From a young age, Japanese students are instilled with a strong work ethic and a commitment to learning. This dedication is reflected in their impressive performance on international assessments like the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA). Japan consistently ranks among the top countries in subjects like mathematics, science projects for kids, and reading for kids, showcasing the effectiveness of their educational methods.
The curriculum in Japan is rigorous and comprehensive, covering a wide range of subjects and topics. This ensures that students receive a well-rounded education, preparing them not only for academic success but also for life beyond the classroom. The emphasis on discipline, perseverance, and problem-solving skills equips Japanese students with valuable tools for success in their future careers.
Global Recognition
The success of the Japanese education system doesn’t go unnoticed on the global stage. Japanese universities are renowned for their high academic standards and cutting-edge research, attracting students and scholars from around the world. Institutions like the University of Tokyo consistently rank among the top universities globally, further cementing Japan’s reputation as an educational powerhouse.
Additionally, Japanese students often excel in international competitions and Olympiads, demonstrating their exceptional skills and knowledge. This global recognition is a testament to the effectiveness of the Japanese education system in nurturing talent and fostering intellectual growth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the enduring legacy of Japanese education is a testament to the power of dedication, innovation, and a deep-rooted respect for learning. Through its rich history and commitment to excellence, Japan has not only shaped its own future but has also inspired the world with its unwavering pursuit of knowledge and character development.
As we look to the future, let us continue to draw inspiration from this remarkable legacy and strive to cultivate the best in ourselves and future generations through education.
To get your hands on more such articles, educational content, and free resources on coding for kids, robotics courses, game development, etc., check out the BrightCHAMPS Blog Page now!
Frequently Asked Questions
A1. Yes, the Japanese Education System is known for its rigorous standards, long study hours, and high expectations for students.
A2. Japanese students cope with academic pressure through discipline, time management, and strong support from teachers and parents. They also often attend “juku” (cram schools) for additional help.
A3. Cultural heritage plays a significant role in the Japanese education system, emphasizing values like respect, diligence, and group harmony. These values are reflected in classroom etiquette and teaching methods.
A4. Yes, there have been recent reforms to reduce stress on students. Some schools have implemented shorter summer vacations and more holistic teaching approaches, focusing on well-being and creativity.
A5. The Japanese education system places a strong emphasis on academic excellence and discipline, which can benefit students in the global job market. However, recent changes also emphasize developing communication and critical thinking skills.
A6. Several successful individuals credit their success to the Japanese education system, including business leaders like Akio Toyoda (Toyota) and Shinya Yamanaka (Nobel laureate in medicine). They often highlight the system’s emphasis on hard work and perseverance.


 We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.
We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.