Financial literacy for Kindergarten is the early introduction of essential money management concepts to young children. It involves teaching them the basics of money, including recognizing different coins and bills, understanding the concept of saving, and making simple decisions about spending. The importance of financial literacy at this stage cannot be overstated, as it provides the foundation for a lifetime of responsible financial choices. It empowers children with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the complex world of money, fostering financial responsibility and independence from a very young age.
In this blog, we’ll explore the importance of financial literacy for kindergarten, highlighting the key role it plays in preparing young children with essential money management skills that will benefit them throughout their lives. We’ll discuss practical strategies and engaging activities to help kindergarteners grasp basic financial concepts, setting them on a path toward financial competence.
Table of contents
- Building Blocks of Financial Literacy for Kindergarteners
- Everyday Lessons Beyond the Classroom
- Financial Literacy Tools for Kindergarten
- Collaboration with Parents and Guardians
- Overcoming Challenges in Teaching Financial Literacy to Kindergarteners
- Assessing Progress and Celebrating Achievements
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions ( FAQs )
Building Blocks of Financial Literacy for Kindergarteners
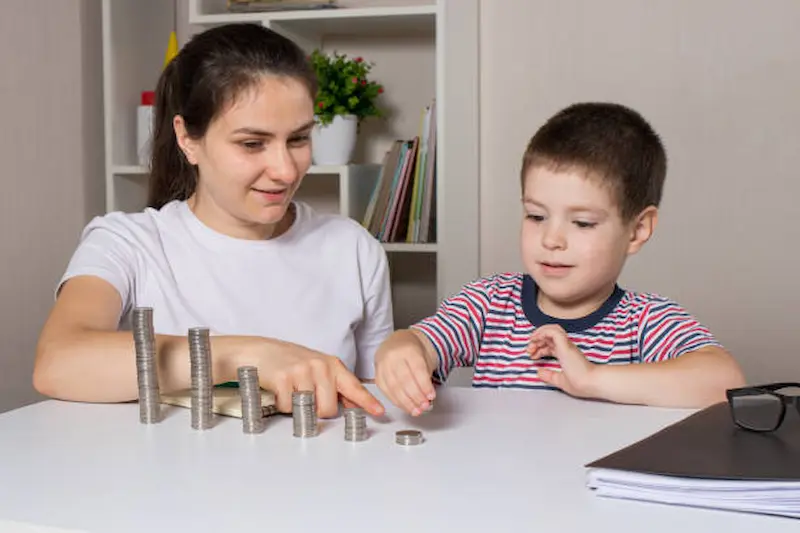

A. Introducing Basic Money Concepts through Play
Kindergarten is the ideal time to start introducing children to basic money concepts through play. Imaginative games can teach them about currency. Incorporate games like “Grocery Store” or “Pretend Shopping” where kids use play money to buy and sell items. This helps them grasp the value of coins and bills.
Additionally, a “Play Store” setup can encourage counting with “money.” Children can take turns being shopkeepers, using fake money to practice addition and subtraction, and honing their math skills while learning about currency.
B. Storytelling for Financial Wisdom
Narratives can be powerful tools for imparting financial wisdom to children, making stories for kids an excellent educational resource. Engage children with stories that revolve around saving and spending. Tales of characters making wise or unwise financial choices help kids understand consequences and decision-making.
Interactive narratives can simplify budgeting basics by involving children in choices made by the story’s characters. This fosters an understanding of how money can be allocated and saved, setting the foundation for a financially literate future.
Everyday Lessons Beyond the Classroom
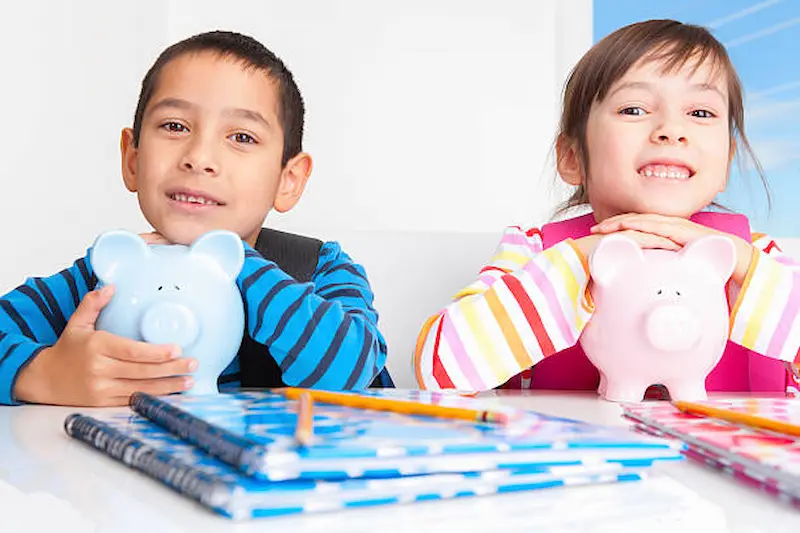

A. Learning Money through Real-Life Experiences
Financial literacy extends beyond the classroom, and everyday experiences can be valuable for teaching kids about money. Take children grocery shopping, involving them in price comparison and budgeting decisions. Encourage them to identify coins and bills while you shop, fostering practical money knowledge that they can apply in real-life situations.
Pocket money is another avenue for financial education. Assign an allowance, letting kids make choices about spending and saving. This hands-on experience empowers them to understand the consequences of financial decisions.
B. DIY Piggy Banks and Savings Jars
Engage children in creative crafts to build their own piggy bank for kids or savings jars. Decorating these encourages ownership and pride in saving. Teach them to set goals for their piggy banks, fostering the concept of saving for a desired reward. These simple, hands-on activities instill lifelong money management skills beyond the classroom, empowering them with the knowledge and habits for responsible financial decisions.
Financial Literacy Tools for Kindergarten
A. Educational Apps and Games
Utilizing educational apps and games can be a fun and effective way to instill financial literacy in kindergarteners, providing engaging educational games for kids. Look for safe and engaging apps designed for early financial education. These apps can introduce children to basic money concepts, like identifying coins and understanding the value of money, making learning an interactive and enjoyable experience.
Interactive games that teach money management skills, such as saving, spending, and budgeting, can make learning an enjoyable experience for kids. They can practice these skills in a virtual setting, which will help them later in real-life financial situations.
B. Age-appropriate books on Financial Literacy
Incorporating age-appropriate books on financial literacy into both the classroom and home activities is crucial. Curate a reading list that includes stories and picture books specifically designed for kindergarteners to learn about money and finances.
Reading these books together can spark discussions about saving, spending, and making wise financial decisions. It’s a valuable way to reinforce financial concepts in a relatable and enjoyable manner. These books serve as essential tools for building a strong foundation of financial literacy in young children.
Collaboration with Parents and Guardians
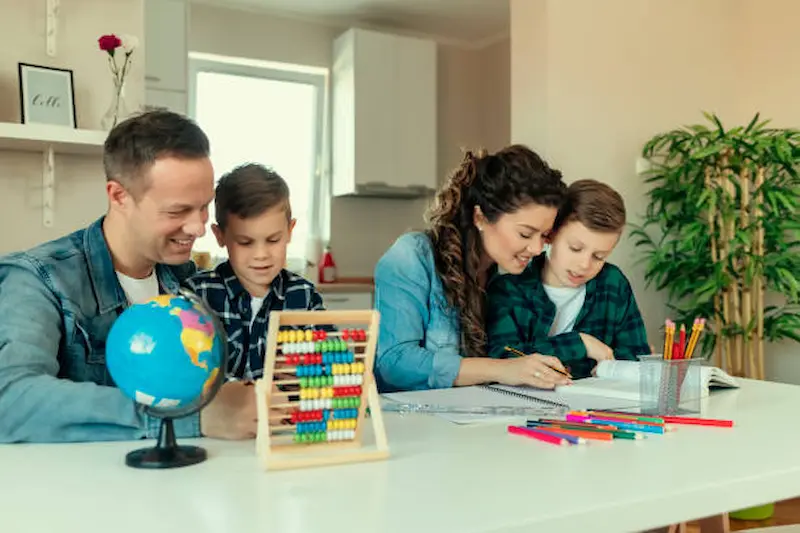

A. Fostering a Partnership for Financial Education
To nurture financial literacy in kindergarteners, it’s essential to create a strong partnership with parents and guardians, emphasizing the importance of financial education for kids. Schools and educators should actively engage families in the process. This partnership can begin with workshops and informational sessions on the importance of financial education at a young age, ensuring that both home and school environments work cohesively to instill these vital life skills in children.
B. Parental Involvement in Reinforcing Classroom Lessons
Encouraging parents to reinforce classroom lessons is paramount, and offering parenting advice is crucial. Provide resources, tips, and activities that parents can easily integrate at home. These might include simple exercises like counting money, discussing savings goals, or practicing responsible spending during family outings. By involving parents in the learning process, children receive consistent messages about financial responsibility and build a strong foundation for their financial future.
Overcoming Challenges in Teaching Financial Literacy to Kindergarteners
A. Addressing Common Misconceptions and Questions
Teaching financial literacy to kindergarteners can present challenges, including common misconceptions and questions for kids. Children may not fully grasp abstract financial concepts. To address this, break down lessons into simple, relatable terms. Explain that money is used to buy things, emphasizing the concept of exchange. Use hands-on activities and visual aids to make these concepts concrete. This approach ensures that young learners can confidently navigate the world of money and finance.
Be prepared for questions that may arise. Encourage children to ask about money, savings, and spending. Answer their queries honestly and age-appropriately. Correct any misconceptions gently, ensuring they have a clear and accurate understanding of financial matters.
B. Adjusting Strategies for Different Learning Styles
Kindergarteners have diverse learning styles, which are crucial for early childhood learning. Some are visual learners, while others are more tactile or auditory. Tailor your teaching strategies to accommodate these differences. Use a variety of materials, such as pictures, charts, and real money, to engage visual learners. Incorporate hands-on activities for tactile learners, like sorting coins or creating savings jars.
For auditory learners, utilize storytelling or discussions about money. Flexibility in your approach ensures that every kindergartener has an opportunity to grasp financial literacy in a way that suits their learning style.
Assessing Progress and Celebrating Achievements

A. Developing Simple Metrics for Financial Understanding
To assess a kindergartener’s progress in financial literacy, it’s important to develop straightforward metrics. This can include their ability to identify different coins and bills, understand the concept of saving, and make basic decisions about spending. Keep records of their achievements, like correctly identifying coins, demonstrating how to save a portion of their allowance, or explaining the idea of “needs vs. wants.” These early lessons in financial literacy for students set the stage for a lifetime of informed money management.
B. Recognizing and Celebrating Financial Milestones
Celebrating financial milestones is essential for reinforcing positive behaviors. When children achieve these metrics, celebrate their accomplishments with praise, encouragement, or small rewards, and don’t forget to include positive affirmations for kids to boost their confidence. Recognizing their efforts and progress helps instill a sense of accomplishment and motivation to continue learning about financial responsibility.
This positive reinforcement is key to building a strong foundation of financial literacy from a young age.
Conclusion
Early financial literacy empowers the next generation with essential skills to navigate an increasingly complex financial world. By introducing basic concepts at a young age, we equip children with the tools they need to make informed decisions about money. Starting early not only imparts knowledge but also fosters a sense of responsibility. Teaching children financial literacy from the outset instills lifelong habits of saving, budgeting, and making wise financial choices, setting the stage for a secure and prosperous future.
To get your hands on more such articles, educational content, and free resources on coding for kids, robotics courses, game development, etc., check out the BrightCHAMPS Blog Page now!
Frequently Asked Questions ( FAQs )
A1. You can introduce basic financial concepts to your kindergartener in a fun and engaging way through imaginative games, like “pretend shopping” or a “play store,” using play money to teach them about currency.
Q2. Are there any age-appropriate games or activities that can help teach financial literacy to my young child?
A2. Yes, there are age-appropriate games and activities, such as educational apps and DIY piggy banks, that can effectively teach financial literacy to young children.
Q3. What are some real-life examples or scenarios that I can use to explain money matters to my kindergarten-aged child?
A3. Use real-life examples like involving your child in grocery shopping, discussing pocket money decisions, or setting up a piggy bank for saving to help explain money matters to your kindergartener.
Q4. Are there any recommended storybooks or resources specifically designed to instill financial understanding in young children?
A4. There are recommended storybooks and resources designed for young children, such as “Berenstain Bears’ Trouble with Money” and “Curious George Saves His Pennies,” which instill financial understanding.
Q5. How can I integrate everyday experiences, like grocery shopping, into teaching my kindergartener about money and budgeting?
A5. You can teach your kindergarteners about money and budgeting by actively involving them in grocery shopping, discussing choices, and explaining how money is spent and saved during everyday experiences.


 We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.
We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.