The Role of Computer Components in Overall System Performance Computer components play a pivotal role in shaping the overall performance of a computer system. Every component, from the central processing unit (CPU) to the graphics card, contributes to the seamless execution of tasks.
A well-coordinated orchestra of components ensures that your computer can handle demanding applications, deliver impressive graphics, and provide swift multitasking capabilities.
Table of contents
- Computer Components
- The Central Processing Unit (CPU): The Brain Behind It All
- Motherboard: The Central Nervous System
- The Basics of RAM Memory: The Short-Term Memory
- Storage Devices: Preserving Your Digital World
- Power Supply: The Unsung Hero
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Where Art Meets Science
- Cooling System: Keeping Your Cool
- Case (Chassis): The Protective Shell
- Input/Output Ports: The Gateway to Connectivity
- Network Interface Card (NIC): Connecting to the World
- Expansion Slots: Room to Grow
- BIOS/UEFI: The Computer’s Startup Guide
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’S)
Computer Components
Main computer components are given below:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Motherboard
- Memory (RAM)
- Storage Device
- Power Supply Unit (PSU)
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPUOptical Drive (Optional)
- Cooling System
- Case (Chassis)
- Input/Output Ports
- Network Interface Card (NIC)
- Expansion Slots
- BIOS/UEFI
The Central Processing Unit (CPU): The Brain Behind It All
At the heart of every computer lies the Central Processing Unit or CPU. Think of it as the brain of your machine. The CPU executes instructions, performs calculations, and manages data, making it the most critical component of your computer.
Introducing machine learning for kids can be an exciting way to help them understand how computers can learn and make decisions on their own.
Motherboard: The Central Nervous System
The motherboard is like the central nervous system, connecting and facilitating communication between all the computer components. It provides a home for the CPU, RAM, and other essential parts. Understanding the motherboard’s layout and components is key to upgrading or building your own computer.
The Basics of RAM Memory: The Short-Term Memory
At the heart of every efficient computing experience lies Random Access Memory (RAM). This integral component is responsible for the swift retrieval of data that the CPU requires for processing. Think of RAM as your computer’s short-term memory, where active applications and tasks are stored for rapid access.
Understanding RAM Memory and Its Crucial Role RAM, often referred to as memory, is like a workspace where data is loaded from storage to be worked on by the CPU. It ensures that your computer can swiftly switch between tasks, run applications smoothly, and maintain the responsiveness users expect.
How RAM Memory Works: Storing and Retrieving Data RAM functions by storing data in cells, each with its unique address. This arrangement allows the CPU to access data directly, without waiting for it to be retrieved from storage devices like hard drives or SSDs.
Different Types of RAM and Their Performance Implications There are various types of RAM available, including DDR4, DDR5, and more. The type and speed of RAM can significantly impact overall system performance. Choosing the right RAM type ensures optimal compatibility and speed for your specific computing needs.
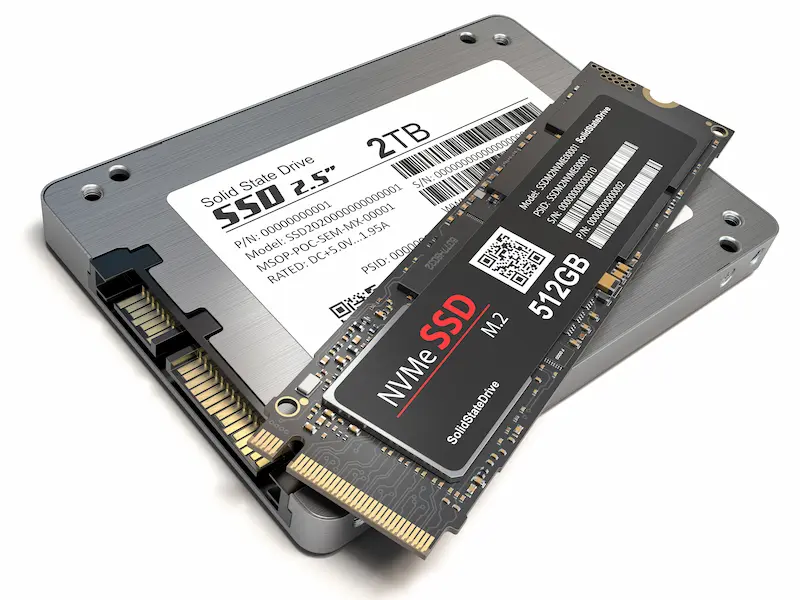
Storage Devices: Preserving Your Digital World
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are the workhorses of data storage. HDDs offer vast storage capacity, while SSDs provide blazing-fast speeds. We’ll delve into the differences between these storage solutions and explore their roles in your computer.
Unveiling Solid-State Drives (SSDs) and Hard-Disk Drives (HDDs)
In the quest for data storage, two contenders stand out:
Solid-State Drives (SSDs) and Hard-Disk Drives (HDDs). Each of these storage options comes with its unique set of advantages and considerations.
- SSDs vs. HDDs: An In-depth Comparison SSDs and HDDs differ fundamentally in their technology. SSDs use flash memory to store data, while HDDs rely on spinning disks and read/write heads. This distinction leads to significant differences in terms of speed, durability, and power efficiency.
- Benefits of SSDs: Speed, Reliability, and Efficiency SSDs have revolutionized data storage with their lightning-fast read and write speeds. They have no moving parts, leading to improved durability and lower power consumption. This makes them an excellent choice for both laptops and desktops, offering improved system responsiveness.
- Advantages of HDDs: Capacity and Affordability HDDs still hold their ground due to their affordability and larger storage capacities. They are ideal for storing large files and applications that don’t require frequent access.

Power Supply: The Unsung Hero
While components like CPUs and GPUs steal the spotlight, the power supply unit (PSU) quietly keeps the entire system running. The PSU’s role goes beyond just delivering electricity – it ensures stability, efficiency, and protection for your computer components.
Power Supply Unit (PSU) Explained: Function and Importance The PSU converts the electricity from your wall outlet into the appropriate voltage and current required by your computer’s components. It’s crucial to choose a PSU that can supply enough power for all your components while maintaining stability.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Where Art Meets Science
If you’re into gaming, digital art activities, or video editing, the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is your best friend. GPUs, play a pivotal role in delivering captivating visual experiences and smooth gameplay for a wide range of games for kids, ensuring vibrant graphics and immersive worlds that spark their imagination.
It’s responsible for rendering stunning visuals and tackling complex calculations, taking your computing experience to the next level.
1) Graphics Card (GPU) Fundamentals: A Visual Powerhouse
If you are going to build gaming PC you must have some knowledge about that. GPUs are specialized processors designed to handle complex graphical computations. They take the load off the CPU and enhance the overall visual experience.
2) Integrated vs. Dedicated GPUs: Choosing the Right Option
Integrated GPUs are built into the CPU and are suitable for everyday tasks, while dedicated GPUs provide superior performance for gaming, content creation, and other graphics-intensive activities.
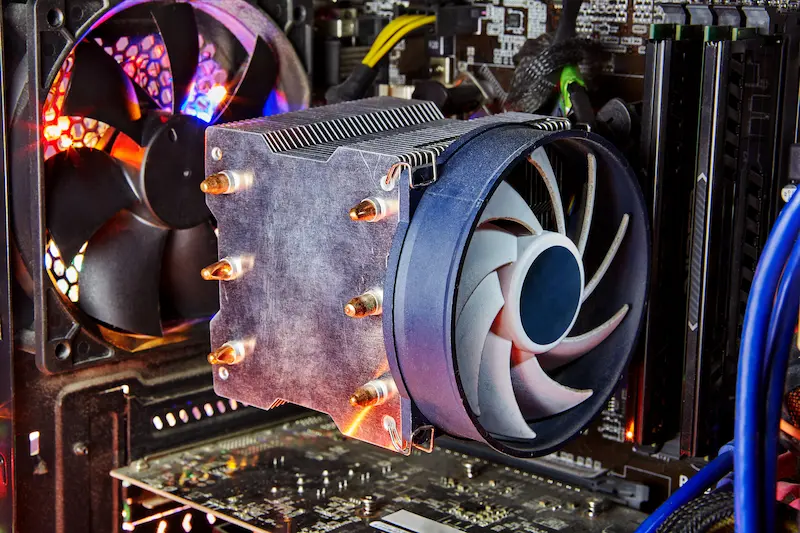
Cooling System: Keeping Your Cool
Computers generate heat, and overheating can lead to performance issues or even hardware damage. Cooling systems, including fans and heat sinks, play a vital role in maintaining the ideal temperature for your components.

Case (Chassis): The Protective Shell
The computer case, or chassis, houses all these components, protecting them from physical damage and dust. It also provides space for additional cooling and expansion options.
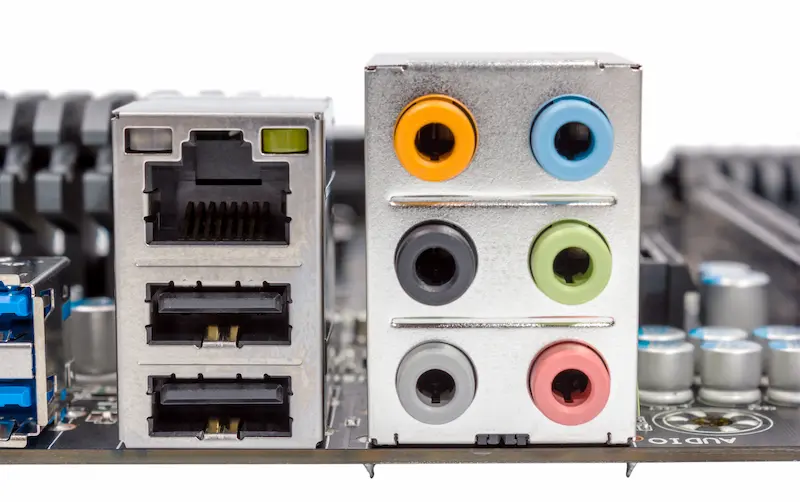
Input/Output Ports: The Gateway to Connectivity
Keyboards, mice, monitors, USB drives, and headphones connect to your computer through input/output ports. These connectors are your gateway to interacting with the digital world and adding external devices.

Network Interface Card (NIC): Connecting to the World
The Network Interface Card (NIC) enables your computer to connect to a network, whether via Ethernet or Wi-Fi. It’s essential for browsing the web, streaming, and online gaming.
Expansion Slots: Room to Grow
Expansion slots on the motherboard allow you to add specialized hardware like sound cards, graphics cards, or network cards. They offer room for customization and future upgrades.
BIOS/UEFI: The Computer’s Startup Guide
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is firmware that kicks off the computer’s startup process. It initializes hardware and provides essential instructions for booting the operating system.
Conclusion
knowledge truly is power. Understanding the intricacies of computer components empowers you to make informed decisions when purchasing, upgrading, or troubleshooting your system.
From the lightning-fast SSDs to the multitasking prowess of CPUs and GPUs, every component plays a vital role in shaping your computing experience. Whether you’re a casual user or a hardcore gamer, this understanding will help you optimize performance, efficiency, and enjoyment.
Join the revolution in education with Brightchamps. Our courses in robotics, coding, and financial literacy empower kids to become confident and capable learners.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’S)
A1. RAM (Random Access Memory) serves as the computer’s temporary workspace. Its primary function is to provide quick access to data that the CPU (Central Processing Unit) needs for processing. RAM allows your computer to run applications smoothly, switch between tasks swiftly, and store data that is actively being used. It’s like a desk where you place items you’re currently working on for easy reach.
A2. SSD (Solid-State Drive) and HDD (Hard Disk Drive) differ in how they store and retrieve data. SSDs use fast flash memory, which allows them to access data almost instantly, making them much faster than HDDs that use spinning disks and read/write heads. SSDs are more durable and energy-efficient, while HDDs offer larger storage capacity at a lower cost.
A3. The power supply unit (PSU) is crucial for system stability because it provides the necessary power to all components. It converts electricity from your wall outlet into the right voltage and current required by your computer. A reliable PSU ensures consistent power delivery, preventing sudden shutdowns, system crashes, and damage to components.
A4. When choosing a graphics card (GPU), consider factors like:
Performance: Look for a GPU that can handle the tasks you need, like gaming or graphic design.
VRAM: More VRAM allows for better handling of high-resolution textures.
Compatibility: Ensure the GPU fits your motherboard and power supply.
Cooling: Check for effective cooling solutions to prevent overheating.
Budget: Choose a GPU that suits your needs without overspending.
A5. Think of the CPU as the “brain” of the computer. It processes instructions and performs calculations necessary for everything your computer does. Just like your brain helps you think and solve problems, the CPU executes tasks like running software, handling calculations, and making sure all the different parts of the computer work together.


 We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.
We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.