As parents, one of the most rewarding and crucial roles we play is in shaping the development and growth of our children. Understanding the various stages of child development can empower us to provide the right support and environment for our little ones to thrive and reach their full potential. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the fascinating world of child development, from prenatal stages to adolescence, and uncover the profound impact it has on lifelong outcomes.
Table of contents
- Introduction to Child Development
- Theories of Child Development
- Prenatal Development: From Conception to Birth
- Infancy: Nurturing the Youngest Minds
- Toddlerhood: Exploring the World
- Preschool Years: Curiosity and Creativity
- Middle Childhood: Expanding Horizons
- Adolescence: Identity and Independence
- Factors Influencing Child Development
- Language Development in Children
- Emotional Development: Nurturing Resilience and Empathy
- Social Development: Building Relationships and Communication Skills
- Physical Development: Gross and Fine Motor Skills
- Cognitive Development: Enhancing Thinking and Learning
- Supporting Children with Special Needs
- Screen Time and Child Development
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to Child Development
Child development is a continuous process that encompasses physical, cognitive, emotional, and social growth. By comprehending the different stages of development, parents can better nurture their children’s unique abilities and needs, ensuring a strong foundation for their future success.
The early years of a child’s life are the most formative and influential. Discover how experiences during this critical period shape a child’s brain development and lay the groundwork for lifelong learning and achievements.
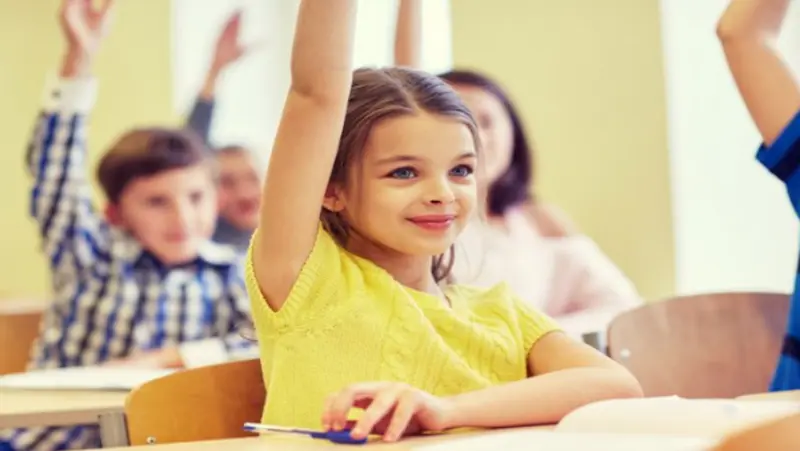

Theories of Child Development
Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development: Stages of Intellectual Growth
Jean Piaget’s groundbreaking theory outlines the distinct stages of cognitive development in children. Understanding these stages can help parents support their children’s intellectual growth and adapt educational strategies accordingly.
Erikson’s Psychosocial Theory: Shaping Social and Emotional Well-Being
Explore Erik Erikson’s psychosocial theory, which focuses on the emotional and social aspects of development. Learn how fostering healthy relationships and emotional well-being can impact a child’s overall development.
Kohlberg’s Theory of Moral Development: Nurturing Ethical Awareness
Morality plays a crucial role in shaping a child’s character. Delve into Lawrence Kohlberg’s theory of moral development and discover strategies for nurturing ethical awareness and empathy in children.
Prenatal Development: From Conception to Birth
The Miracle of Life: Stages of Prenatal Growth
Prenatal development is a miraculous journey that lays the foundation for a child’s life. Learn about the various stages of development from conception to birth and how parents can support healthy growth during pregnancy.
Influences on Prenatal Development: Nutrition, Environment, and Maternal Health
Discover the factors that influence prenatal development, including maternal nutrition, environmental factors, and maternal health. Understanding these influences can help parents make informed choices to support optimal development.
Infancy: Nurturing the Youngest Minds
Milestones in Infant Development: From Smiling to Walking
The first year of life is marked by incredible milestones. Explore the physical, cognitive, and emotional developments during infancy, from the first smile to those precious first steps.
Attachment and Bonding: The Building Blocks of Emotional Security
Building a strong bond with your infant is crucial for their emotional well-being. Learn about the importance of attachment and how nurturing this bond fosters a sense of security and self-esteem.
Toddlerhood: Exploring the World
Language Explosion: From First Words to Sentences
Toddlers experience a language explosion, and communication becomes more sophisticated. Discover strategies to encourage language development and support your child’s expanding vocabulary.
Independence and Autonomy: Fostering Self-Reliance
As toddlers explore their independence, they develop vital life skills. Learn how to strike a balance between providing support and encouraging autonomy to help them grow confidently.

Preschool Years: Curiosity and Creativity
Cognitive Skills: Preparing for School Readiness
Preschoolers are eager learners with curious minds. Explore activities that enhance cognitive development and prepare children for a successful transition to school.
Social Interaction: Making Friends and Cooperative Play
Preschool years are when children start engaging in more social interactions. Discover how parents can encourage positive socialization and teach essential cooperation skills.
Middle Childhood: Expanding Horizons
Cognitive Advancements: Abstract Thinking and Problem-Solving
Middle childhood is a period of significant cognitive growth. Learn about fostering abstract thinking and problem-solving abilities to help children excel academically and creatively.
Emotional Intelligence: Understanding and Managing Feelings
Emotional intelligence is critical for building healthy relationships. Explore ways to help your child understand and manage their emotions effectively.
Adolescence: Identity and Independence
Puberty and Physical Changes: Navigating the Teenage Years
Adolescence is a time of profound physical and hormonal changes. Learn how to support teenagers through this transformative phase and address their unique needs.
Peer Influence and Social Identity: Shaping Adolescent Behavior
Friends and peers play a significant role in shaping teenagers’ behavior. Discover how parents can guide their adolescents to make positive choices and develop a strong sense of self.
Factors Influencing Child Development
1. Nature vs. Nurture: The Interplay of Genetics and Environment
One of the most significant factors influencing child development is the interplay between nature (genetics) and nurture (environment). Genetics contribute to a child’s inherent traits, such as physical appearance, temperament, and cognitive abilities.
However, the environment in which a child is raised, including family, school, community, and cultural influences, also plays a crucial role in shaping their development. Understanding this interplay helps parents and caregivers recognize the unique needs of each child and tailor their support accordingly.

2. The Impact of Parenting Styles: Authoritative, Permissive, and More
Parenting styles significantly influence a child’s emotional, social, and cognitive development. Authoritative parenting, characterized by warmth, clear boundaries, and consistent discipline, fosters a balanced and secure environment for children to explore and learn.
On the other hand, permissive parenting, which involves lenient rules and low demands, may lead to challenges in setting boundaries and self-discipline. Different parenting styles impact a child’s self-esteem, communication skills, and ability to handle challenges, emphasizing the importance of a nurturing and supportive parenting approach.
3. Socioeconomic Status and Family Environment
The socioeconomic status (SES) of a family and the overall family environment can have a profound impact on a child’s development. Children from low-SES families may face challenges such as limited access to quality education, healthcare, and resources, which can affect their academic and cognitive development.
Conversely, children from higher-SES families may have more opportunities for enrichment activities, leading to greater cognitive and social advantages. Creating a supportive and nurturing family environment regardless of SES can help mitigate potential disparities.
4. Early Childhood Experiences
Early childhood experiences, especially during the first five years of life, lay the foundation for a child’s development. Positive experiences, such as secure attachments, responsive caregiving, and engaging stimulation, promote healthy brain development and emotional well-being.
On the other hand, adverse experiences, such as neglect, abuse, or exposure to trauma, can have long-lasting effects on a child’s physical and mental health. Providing a safe and loving environment during early childhood is crucial for fostering healthy development.
5. Peer Influence and Social Interactions
As children grow older, their interactions with peers become increasingly influential in shaping their behaviors and attitudes. Positive peer relationships can foster social skills, empathy, and cooperation, while negative peer influences may lead to risky behaviors or social challenges.
Encouraging healthy friendships and providing opportunities for positive social interactions can support a child’s social development and emotional well-being.
Understanding these influential factors in child development empowers parents, caregivers, and educators to create a nurturing and supportive environment that maximizes a child’s potential. By recognizing the interplay of genetics, parenting styles, family environment, early experiences, and peer influence, we can lay the groundwork for healthy growth and lifelong success.
Language Development in Children
1. Language Acquisition: From Babbling to Fluent Communication
Language acquisition is a fascinating process that begins at birth and evolves as children grow. During the early months, infants engage in babbling, a precursor to spoken language. As they progress, they start imitating sounds and eventually form their first words.
By the age of three, most children have developed basic language skills and can communicate in short sentences. As parents and caregivers, providing a language-rich environment, reading to children, and engaging in meaningful conversations play a vital role in supporting their language development during these critical early years.

2. Bilingualism and Multilingualism: Benefits and Challenges
Many children are raised in bilingual or multilingual environments, exposed to more than one language from a young age. Research suggests that bilingualism offers numerous cognitive benefits, such as enhanced executive functions, better problem-solving skills, and improved mental flexibility.
Bilingual children also tend to have more extensive cultural awareness and appreciation. However, bilingualism may present challenges such as code-switching (shifting between languages), initially slower vocabulary development in each language, and potential confusion in language use. Nevertheless, with consistent exposure and support, bilingual children can navigate both languages proficiently and reap the long-term advantages of being bilingual.
3. Language Development Disorders and Speech Delay
Some children experience language development disorders or speech delays, where they struggle with acquiring language skills at a typical rate. These conditions may be caused by various factors, including developmental issues, hearing impairments, or neurological conditions.
Early identification and intervention are crucial in such cases. Speech therapy and other specialized interventions can help children overcome language challenges, improve their communication skills, and build their confidence.
Emotional Development: Nurturing Resilience and Empathy
Emotional Regulation: Coping with Feelings and Stress
Help your child build emotional resilience by teaching them effective coping mechanisms to manage stress and difficult emotions.
Building Empathy: Fostering Compassion and Understanding
Empathy is a crucial skill that enhances social relationships. Discover activities that foster empathy and compassion in children.
Social Development: Building Relationships and Communication Skills
Play and Socialization: The Importance of Peer Interaction
Play is more than just fun; it’s a vital aspect of social development. Learn how playtime with peers enhances social skills and promotes healthy relationships.
Social Skills Training: Enhancing Communication and Conflict Resolution
Equip your child with essential social skills that will help them communicate effectively, resolve conflicts, and build strong interpersonal connections.
Physical Development: Gross and Fine Motor Skills
Gross Motor Skills: Mastering Movement and Coordination
Encourage physical activity and play to develop your child’s gross motor skills and improve coordination and balance.
Fine Motor Skills: The Development of Dexterity and Precision
Discover activities that enhance fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination, laying the groundwork for essential life skills like writing and drawing.

Cognitive Development: Enhancing Thinking and Learning
Cognitive Stimulation: Activities to Boost Brain Development
Engage your child in stimulating activities that promote cognitive development and enhance their ability to think critically and creatively.
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking: Nurturing Intellectual Growth
Foster problem-solving and critical thinking skills in children to prepare them for academic success and real-life challenges.
Supporting Children with Special Needs
1. Identifying Developmental Delays: Early Intervention and Support
Early identification of developmental delays in children is crucial for providing timely interventions and support. Regular developmental screenings and assessments help identify any potential challenges or delays in areas such as motor skills, speech and language, social-emotional development, and cognitive abilities.
When delays are detected early, children can receive targeted interventions and therapies that can make a significant difference in their progress. Early intervention programs, including physical therapy, speech therapy, occupational therapy, and behavioral interventions, are designed to address specific needs and help children reach their developmental milestones.
2. Inclusive Education: Creating Supportive Learning Environments
Inclusive education is a vital approach that emphasizes providing equal opportunities and support to children with special needs within the regular classroom setting. Inclusive classrooms welcome children with diverse abilities, and educators receive training to accommodate various learning styles and needs.
By creating supportive learning environments, children with special needs can learn alongside their typically developing peers, fostering social inclusion, acceptance, and understanding. Inclusive education also promotes positive interactions and friendships, which can have a profound impact on a child’s self-esteem and overall well-being.
3. Collaborative and Individualized Education Plans
Collaboration between parents, educators, and specialists is essential in supporting children with special needs. Individualized Education Plans (IEPs) or Individualized Family Service Plans (IFSPs) are customized plans that outline specific goals, accommodations, and services for children with special needs.
These plans are designed to address the unique challenges and strengths of each child and provide a roadmap for their education and development. Regular progress monitoring and communication between all stakeholders ensure that the child’s needs are met effectively, and appropriate adjustments are made as needed.
Screen Time and Child Development
Balancing Digital Devices: The Impact of Screen Time on Development
Explore the effects of excessive screen time on child development and learn how to strike a healthy balance between digital devices and other activities.
Guidelines for Healthy Media Use: Promoting Balanced Growth
Establish guidelines for media usage to ensure children benefit from technology while minimizing potential negative impacts.
Conclusion
As we conclude this journey through child development, let us reflect on the importance of understanding and supporting each stage to unlock the full potential of our children. By embracing the power of child development, we can create a nurturing environment that fosters growth, resilience, and success throughout their lives. Together, let’s embark on this empowering journey of parenting and unleashing our children’s true potential.
To get your hands on more such educational and free resources on coding for kids, robotics courses for kids, game development, etc., do check out the Brightchamps Page now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Key milestones in child development include sitting, crawling, walking, first words, forming sentences, social interactions, problem-solving, emotional regulation, and abstract thinking.
Parents can promote language development by talking, reading, and singing to their child regularly, engaging in conversations, using descriptive language, and providing a language-rich environment.
Effective parenting strategies for supporting emotional development include offering emotional support, validating feelings, setting boundaries, teaching coping skills, and being a positive role model for handling emotions.
To identify developmental delay, observe if your child misses age-appropriate milestones, shows limited speech, has difficulty with social interactions, or struggles with motor skills. Consult a pediatrician for evaluation and early intervention.
Encourage social growth by arranging playdates, participating in group activities, and teaching cooperation. Foster cognitive growth through age-appropriate games, puzzles, reading, and encouraging curiosity and exploration.


 We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.
We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.