Teaching children effective anger management skills is of paramount importance in today’s society. Anger is a natural human emotion that can arise in response to various triggers, such as frustration, injustice, or disappointment.
While it is normal for children to experience anger, it is crucial to equip them with the necessary tools to manage and express their anger in a healthy and constructive manner. By instilling these skills early on, we can empower children to navigate their emotions, build healthier relationships, and contribute positively to their personal and social development.
One significant reason why teaching children effective anger management skills is vital is that it promotes emotional intelligence. Emotional intelligence encompasses the ability to recognize, understand, and regulate one’s own emotions and empathize with others.
By teaching children how to manage anger, we help them develop a deeper understanding of their emotions, enabling them to identify triggers, assess their emotional state, and respond appropriately. This emotional awareness allows children to communicate their needs and concerns effectively, leading to healthier interactions and improved relationships with peers, family members, and authority figures.
In addition, teaching children how to manage anger effectively contributes to their overall mental health and well-being. Uncontrolled or poorly managed anger can have detrimental effects on a child’s emotional and psychological state. It can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and even depression.
By providing children with strategies to cope with anger, such as deep breathing, self-reflection, or seeking support from trusted individuals, we empower them to regulate their emotions and maintain a positive mental state. This, in turn, enhances their overall well-being, promotes a sense of self-control, and reduces the likelihood of developing long-term mental health issues.
Table of contents
- Understanding Childhood Anger
- Common triggers of anger in children
- The impact of unmanaged anger on children
- Signs of Anger Issues in Children
- Effective Anger Management Strategies for Kids
- Encourage problem-solving skills
- Practice healthy coping mechanisms
- Set clear and consistent boundaries
- Consistency and Discipline
- Conclusion:
- Frequently Asked Questions
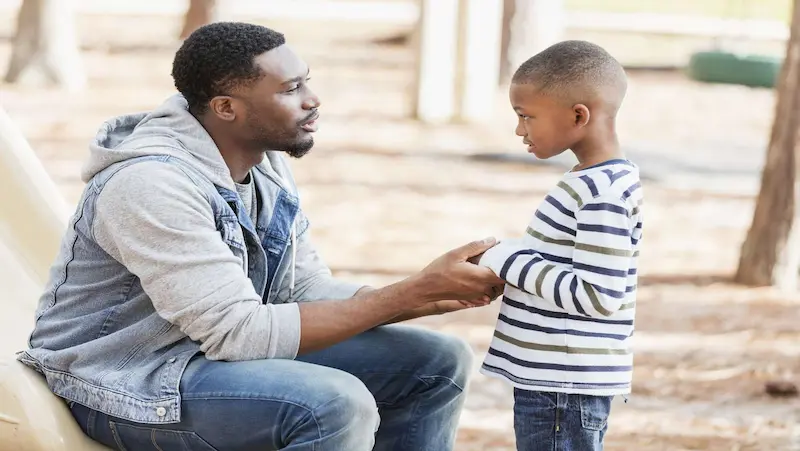
Understanding Childhood Anger
Childhood is a time of exploration, learning, and emotional growth. Along this journey, children encounter a wide range of emotions, including anger. Anger is a natural and common emotion experienced by children and adults alike.
Teaching kids about emotions including anger management, is essential for their emotional intelligence. Equipping them with tools to identify, understand, and express their feelings helps them navigate challenging emotions like anger in healthy and constructive ways.
However, it is essential to understand the nature of childhood anger and differentiate between normal expressions of anger and problematic anger issues. This blog aims to shed light on childhood anger, its purpose, and how to distinguish between healthy anger and concerning anger problems.

Anger as a Natural Emotion:
Anger is a basic human emotion that serves a purpose in our lives. It is a normal reaction to perceived threats, injustices, or frustrations. In childhood, anger often arises when a child feels misunderstood, frustrated, or powerless in a given situation. It can be triggered by various factors such as conflicts with peers or siblings, academic challenges, changes in routine, or unmet desires.
Teaching kids patience involves helping them understand that anger is a natural emotion and providing them with strategies to manage it effectively. By learning to recognize triggers and practicing techniques such as deep breathing and positive self-talk, children can develop valuable skills to handle their emotions in a balanced and composed manner.
Understanding the Purpose of Anger:
Anger, when expressed appropriately, can be a healthy emotional response. It acts as a signal to indicate that something is wrong or needs attention. By expressing anger, children can assert themselves, communicate their needs, and establish boundaries. It also helps children develop problem-solving skills as they learn to address the underlying causes of their anger.
Differentiating Normal Anger from Problematic Anger Issues:
While anger is a natural emotion, it is crucial to identify when it becomes problematic and potentially harmful to a child’s well-being. Here are some key distinctions between normal anger and problematic anger issues:
Intensity and Duration: Normal anger tends to be temporary and proportional to the triggering event. It subsides once the child expresses their emotions or finds a resolution. Problematic anger, on the other hand, maybe excessively intense, prolonged, and disproportionate to the situation.
Frequency and Triggers: Occasional anger outbursts are a normal part of childhood. However, if a child frequently displays anger, reacts intensely to minor triggers, or exhibits aggression towards others or themselves, it may indicate an anger issue.
Impact on Daily Functioning: Normal anger does not significantly disrupt a child’s daily life or relationships. Problematic anger, however, can interfere with their social interactions, academic performance, and overall well-being.
Unhealthy Expression: Healthy anger involves expressing emotions appropriately, such as through assertive communication or seeking support from trusted adults. Problematic anger, on the other hand, may manifest as physical aggression, verbal abuse, self-harm, or property destruction.
Other Emotional and Behavioral Issues: Problematic anger can be linked to other emotional or behavioral difficulties, such as chronic irritability, impulsivity, defiance, or difficulties with emotional regulation.
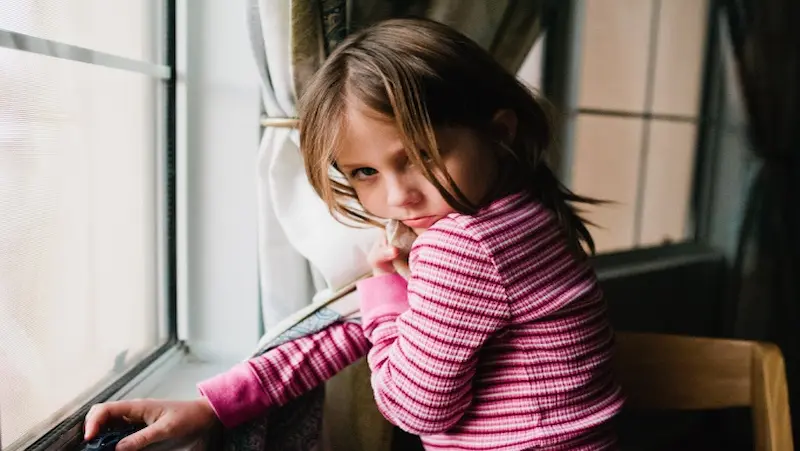
Common triggers of anger in children
Anger is a natural and valid emotion experienced by individuals of all ages, including children. As parents, caregivers, or educators, it is essential to recognize and understand the common triggers that can provoke anger in children.
By identifying these triggers, we can effectively support and guide children in managing their emotions. In this blog, we will explore some of the typical situations or events that can ignite anger in kids and discuss strategies to help them navigate through these challenges.

Frustration due to lack of control:
Children often feel angry when they encounter situations where they have little control. This can include being unable to complete a task, facing limitations due to their age, or feeling restricted by rules and regulations.
The frustration resulting from the inability to meet their desires or expectations can quickly escalate into anger. It is crucial to provide children with age-appropriate autonomy and opportunities for decision-making to reduce their feelings of powerlessness.
Feeling misunderstood or unheard:
Children, like adults, desire to be heard and understood. When they perceive a lack of validation for their thoughts, feelings, or opinions, it can lead to anger. Inadequate communication or dismissing their emotions may exacerbate their frustration. Fostering positive thinking for kids is crucial, especially when they’re feeling misunderstood or unheard. Encouraging them to focus on their strengths, problem-solving abilities, and the potential for growth can empower them to overcome challenges and communicate their feelings in a constructive and confident manner.
Active listening, empathy, and open dialogue play pivotal roles in ensuring children feel acknowledged and respected.
Fatigue and hunger:
Just like adults, children are susceptible to irritability when they are tired or hungry. Lack of proper rest or nutrition can lower their threshold for managing emotions, making them more prone to anger. Maintaining regular sleep patterns and providing healthy snacks can significantly contribute to stabilizing their mood and reducing outbursts.
Balanced kids’ nutrition plays a role in anger management. Providing nourishing meals and snacks can contribute to stable blood sugar levels, reducing mood swings and potential triggers for anger outbursts.
Challenging transitions and changes:
Teaching anger management for kids becomes particularly important during challenging transitions and changes. Transitions can be particularly challenging for children, triggering a sense of discomfort and unease. Moving to a new school, changing homes, or experiencing significant alterations in routine can induce feelings of anxiety and anger.
Offering support during these transitions, establishing predictable routines, and communicating openly about the changes can help children adapt and manage their emotions more effectively.
Unrealistic expectations:
Children, especially younger ones, may struggle with managing their emotions when faced with unrealistic expectations. Pressure to achieve academic success, perform well in extracurricular activities, or meet excessively high standards can create feelings of stress and frustration, leading to angry outbursts.
Encouraging a balanced approach, emphasizing effort over outcome, and celebrating small victories can help alleviate the pressure children may feel.
Emotional and social challenges:
Children may encounter emotional or social difficulties that trigger anger. Bullying, peer conflicts, or feeling excluded can provoke intense emotional responses. It is crucial to teach children healthy ways to express their emotions and equip them with effective problem-solving skills. Engaging in emotional regulation activities for kids can greatly benefit their well-being.
Encouraging positive social interactions and fostering an inclusive environment can also mitigate anger triggers related to social situations.
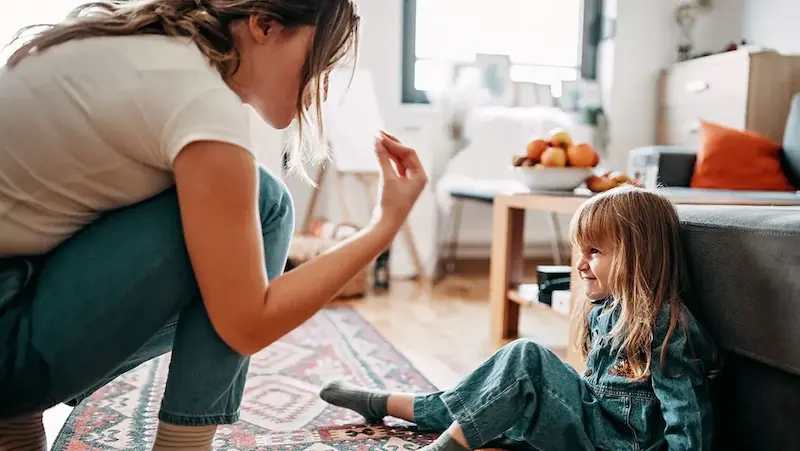
The impact of unmanaged anger on children
Anger is a natural emotion experienced by everyone, including children. However, when anger remains unmanaged and unresolved, it can have detrimental effects on a child’s well-being and overall development. Parenting style greatly influences a child’s development. The impact of unmanaged anger on children can be profound, potentially leading to emotional distress, strained relationships, and hindered emotional growth.
Uncontrolled anger not only impacts the child’s immediate emotional state but also has far-reaching consequences that can affect their relationships, behavior, and mental health.
In this blog, we will delve into the negative consequences of unmanaged anger and highlight the importance of teaching children healthy ways to express and manage their emotions.

Emotional Instability
When anger goes unmanaged, it can lead to emotional instability in children. Unresolved anger may manifest as frequent outbursts, irritability, and a generally volatile emotional state.
Children who struggle with uncontrolled anger often find it challenging to regulate their emotions, leading to a rollercoaster of intense feelings. This emotional instability can hinder their ability to establish healthy relationships, manage stress, and cope with daily challenges.
Impaired Social Skills
Unmanaged anger can significantly impact a child’s social skills and interactions with others. When children consistently express anger in inappropriate ways, such as aggressive behavior or verbal outbursts, their peers may distance themselves, leading to feelings of isolation and low self-esteem.
Additionally, unresolved anger can inhibit the development of essential social skills such as empathy, active listening, and conflict resolution, making it difficult for children to form and maintain positive relationships.
Academic Challenges
Anger that remains unmanaged can also affect a child’s academic performance. When a child is consumed by anger, their ability to concentrate, focus, and retain information can be compromised.
The resulting difficulty in learning and problem-solving can lead to academic struggles and a negative impact on their overall educational experience. Additionally, unmanaged anger may contribute to disruptive behaviors in the classroom, further hindering their academic progress.
Physical Health Issues
Unresolved anger can take a toll on a child’s physical health. Frequent anger and stress can trigger physiological responses such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and weakened immune system.
Prolonged exposure to these physical reactions can make children more susceptible to illnesses and weaken their overall health. Moreover, uncontrolled anger can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as emotional eating or self-harm, which further compromise their well-being.
Long-Term Mental Health Challenges
Perhaps one of the most concerning consequences of unmanaged anger is its potential impact on a child’s long-term mental health. Unresolved anger has been linked to various mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and even aggression-related disorders.
These conditions can persist into adulthood, affecting the individual’s overall quality of life, relationships, and future success. By addressing anger issues early on and teaching children healthy coping mechanisms, we can help mitigate the risk of long-term mental health challenges.
Signs of Anger Issues in Children
Identifying the signs of anger problems is crucial for individuals and their loved ones, as it can help in understanding and managing this powerful emotion.
In this blog, we will explore some of the behavioral signs that may indicate an individual is struggling with anger problems, particularly focusing on outward expressions of anger, such as tantrums, aggression, and defiance. By recognizing these signs, we can begin to address and channel anger in healthier ways.
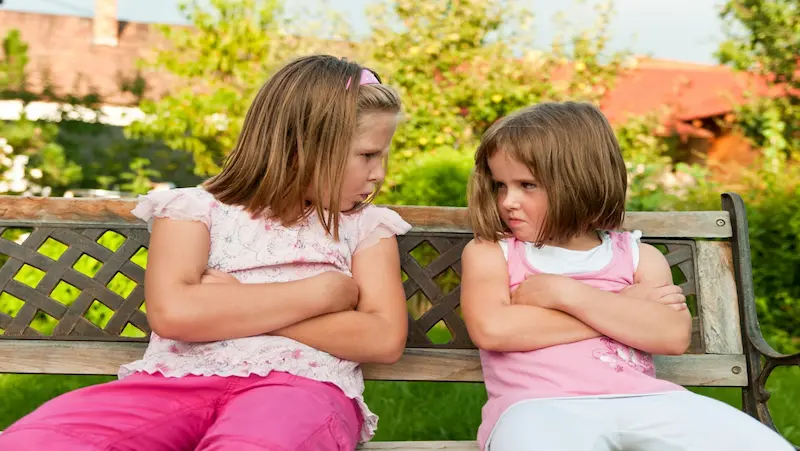

Frequent and Intense Tantrums:
One of the primary behavioral signs of anger problems is the manifestation of frequent and intense tantrums, often characterized by explosive outbursts of anger. These tantrums may occur in both children and adults, albeit with varying degrees of severity.
During a tantrum, an individual may yell, scream, throw objects, or engage in physical aggression toward others or themselves. These outbursts can be triggered by seemingly minor frustrations or perceived injustices. Recognizing the frequency and intensity of tantrums is essential in identifying underlying anger issues.
Aggression and Hostility:
Another common behavioral sign of anger problems is the display of aggressive behavior. This can manifest in physical aggression, such as hitting, kicking, or throwing objects, as well as verbal aggression, such as yelling, insulting, or threatening others.
Aggressive behavior often serves as a release for built-up anger and can be particularly destructive to relationships and personal well-being. Individuals struggling with anger problems may find it challenging to control their aggression and may harm others or themselves in the process.
Defiance and Opposition:
Individuals with anger problems may frequently display defiance and opposition towards authority figures or rules. They may challenge and resist rules, instructions, or requests, often engaging in confrontations or arguments.
This rebellious behavior can stem from an underlying sense of frustration and anger towards perceived limitations or constraints. Persistent defiance can lead to strained relationships, workplace conflicts, and academic or legal consequences.
Impatience and Irritability:
Anger problems can also manifest in the form of chronic impatience and irritability. Individuals experiencing anger issues often have a low tolerance for frustration and may become easily agitated by minor inconveniences or delays.
They may display irritability through snappy remarks, sarcastic comments, or constant complaining. This behavior not only affects their own well-being but also creates a tense environment for those around them.
Emotional Withdrawal and Isolation:
While anger is commonly associated with explosive and aggressive behavior, it can also manifest as emotional withdrawal and isolation. Some individuals struggling with anger problems may suppress their anger, leading to a more inward expression of this emotion.
They may become emotionally distant, avoid social interactions, and withdraw from activities they once enjoyed. This withdrawal is often an attempt to avoid confrontations or prevent outbursts, but it can further exacerbate feelings of anger and isolation.
Effective Anger Management Strategies for Kids
In today’s fast-paced and technology-driven world, emotional intelligence is more crucial than ever. The ability to understand and communicate our emotions effectively not only improves our personal relationships but also contributes to our overall well-being.
Incorporating specific kids’ activities focused on anger management can be highly beneficial. Activities like journaling about emotions, practicing deep-breathing exercises, or engaging in role-play scenarios help children understand and express their anger in healthy ways, promoting emotional awareness and effective communication skills.
As adults, we have a responsibility to teach children how to recognize and express their emotions, empowering them to navigate their emotional landscape with confidence. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of teaching emotion recognition and communication to children and provide practical tips to help them on this journey of self-discovery.
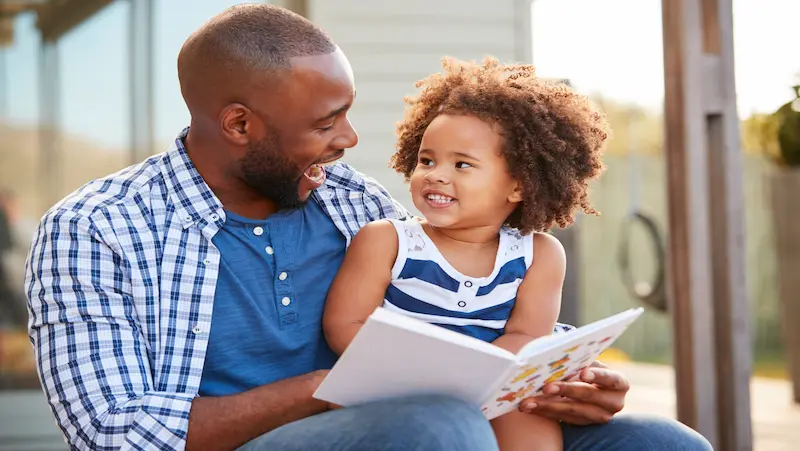

The Importance of Emotion Recognition:
Emotion recognition is the first step towards understanding and managing our feelings. Children who are aware of their emotions can develop a better understanding of themselves and others.
By recognizing different emotions, they become more empathetic and compassionate individuals, which leads to healthier relationships and improved social skills. Emotion recognition also plays a significant role in mental health and self-regulation, enabling children to cope with stress, frustration, and anxiety more effectively.
Creating a Safe and Supportive Environment:
Building a safe and supportive environment is crucial when teaching children about emotions. Encourage open and honest communication by creating an atmosphere where emotions are accepted and respected.
Help children understand that it is normal to feel a wide range of emotions and that all emotions are valid. By doing so, you foster an environment where children feel comfortable expressing their feelings without fear of judgment or rejection.
Building Emotion Vocabulary:
One of the first steps in teaching emotion recognition is to build a vocabulary of emotions. Start with basic emotions such as happiness, sadness, anger, fear, and surprise. Use books, picture cards, or online resources that depict different facial expressions associated with these emotions.
Engage children in discussions, asking them how they would feel in certain situations. This helps them connect their experiences with specific emotions, expanding their emotional vocabulary.
Identifying and Validating Emotions:
Once children have a basic understanding of different emotions, help them identify and label their own feelings. Encourage them to express their emotions by asking open-ended questions like, “How do you feel about that?” or “What emotions are you experiencing right now?” Validate their emotions by acknowledging and accepting their feelings, even if you don’t fully understand why they feel that way.
Validating their emotions helps children develop a sense of self-worth and builds trust in their ability to communicate their feelings.
Non-Verbal Cues and Body Language: Emotions are not just expressed through words; they are also communicated through non-verbal cues and body language. Teach children to pay attention to these cues, such as facial expressions, tone of voice, and body posture.
Engage in activities like role-playing or charades to help them recognize and interpret these non-verbal cues. Understanding non-verbal communication enhances their empathy skills, as they can better comprehend others’ emotional states.
Developing Emotional Regulation Strategies:
Teaching children how to regulate their emotions is an essential aspect of emotional intelligence. Encourage them to explore healthy coping mechanisms, such as deep breathing exercises, journaling, drawing, or engaging in physical activities.
Provide them with a toolbox of strategies they can use when they feel overwhelmed or anxious. By teaching them how to manage their emotions, you empower them to navigate challenging situations more effectively.
Encourage problem-solving skills
As parents and educators, one of our primary goals is to raise children who are equipped with essential life skills, including problem-solving. Cultivating problem-solving skills not only helps children navigate challenges effectively but also empowers them to address the root causes of their emotions.
Teaching conflict resolution skills for kids teaching them responsibility, such as problem-solving techniques, empowers them to navigate disagreements constructively.
In this blog, we will focus on teaching children how to identify and address the underlying causes of their anger. By doing so, we can guide them towards healthier emotional expression and provide them with lifelong tools for resolving conflicts.
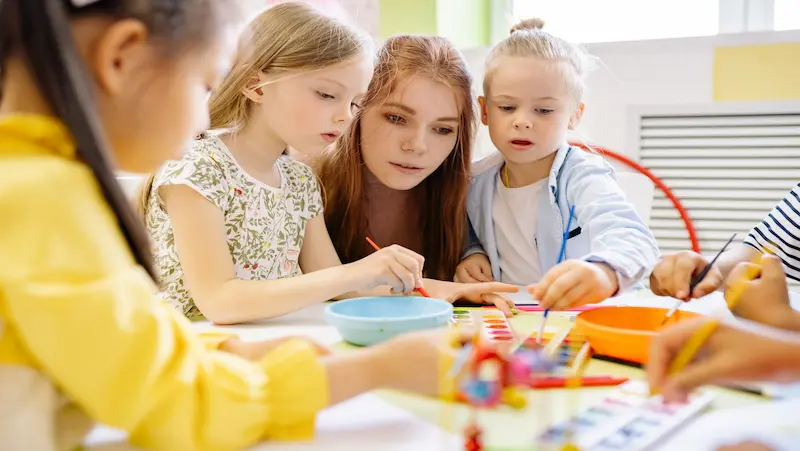

Understanding the Nature of Anger:
Anger is a natural human emotion, and children, like adults, experience it in response to various triggers. However, children may struggle to identify the underlying causes of their anger, leading to frequent outbursts or unproductive responses.
By encouraging problem-solving skills, we can help children develop a deeper understanding of their emotions and provide them with constructive ways to manage their anger.
Create a Safe Environment for Open Communication: Establishing a safe and supportive environment is crucial for children to feel comfortable expressing their emotions. Encourage open communication by actively listening to your child, validating their feelings, and avoiding judgment. When children feel heard and understood, they are more likely to engage in discussions about their anger and its underlying causes.
Teach Emotional Awareness: Help children develop emotional awareness by teaching them to identify and label their emotions. Create a feelings chart or use picture cards to assist younger children in recognizing different emotions. By understanding and acknowledging their anger, children can begin to explore why they feel that way and what triggers it.
Identify Triggers: Guide children in identifying the triggers that lead to their anger. These triggers could be specific situations, events, or even certain people. Encourage them to reflect on their experiences and help them connect the dots between the trigger and their emotional response. This process helps children gain insight into the root causes of their anger.
Explore Underlying Causes: Once the triggers are identified, help children delve deeper into the underlying causes of their anger. Teach them that anger is often a secondary emotion, masking underlying feelings such as frustration, sadness, or disappointment. Encourage them to explore what lies beneath their anger and discuss alternative ways to express those emotions.
Encourage Problem-Solving: Teach children problem-solving techniques that they can apply when they experience anger. Help them brainstorm possible solutions to the underlying issues causing their anger and discuss the pros and cons of each option. This process fosters critical thinking skills and empowers children to take control of their emotions and responses.
Practice Conflict Resolution: Engage children in role-playing activities or hypothetical scenarios that involve conflicts. Encourage them to come up with peaceful and constructive resolutions, promoting empathy and understanding. By practicing conflict resolution, children develop the skills needed to handle anger-inducing situations in a more effective and compassionate manner.
Model Effective Problem-Solving: Children learn by observing the behavior of adults around them. Be a positive role model by demonstrating effective problem-solving skills in your own life. When faced with challenges or conflicts, talk aloud about how you identify the underlying causes, brainstorm solutions, and choose the best course of action. By witnessing these problem-solving techniques, children are more likely to internalize and apply them to their own experiences.
Practice healthy coping mechanisms
In our fast-paced and often stressful lives, it’s essential to have effective coping mechanisms to manage negative emotions. Anger, in particular, can be a powerful and overwhelming emotion, but it doesn’t have to consume us. One of the most beneficial ways to deal with anger is through physical activity and exercise.
Not only does it provide a healthy outlet for our emotions, but it also offers numerous physical and mental health benefits. In this blog, we will explore the connection between physical activity and anger management, highlighting the importance of incorporating exercise into our daily routines.
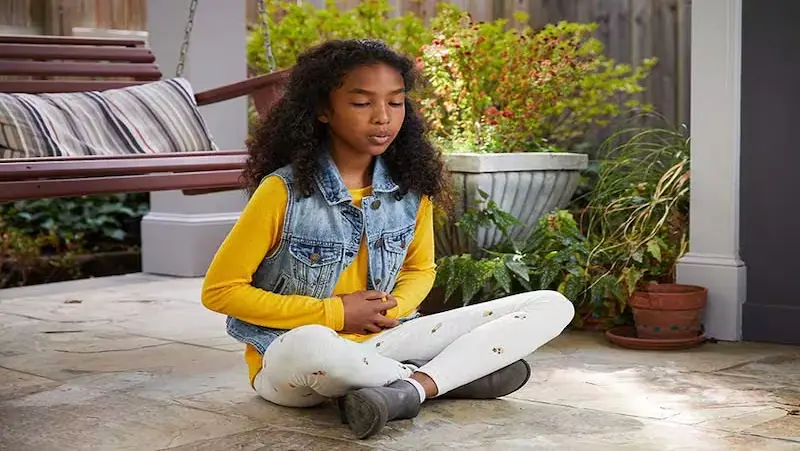

The Role of Physical Activity:
Physical activity and exercise have long been recognized for their positive impact on mental health. Engaging in regular physical activity not only helps maintain a healthy body but also promotes emotional well-being and reduces stress.
When it comes to anger management, physical activity serves as a productive outlet, channeling the intense energy associated with anger into a constructive and controlled form of expression.
Benefits of Exercising to Manage Anger:
Release of Endorphins: Exercise triggers the release of endorphins, which are natural mood-boosting chemicals in the brain. These endorphins promote a sense of well-being, reduce stress, and alleviate symptoms of anger.
Stress Reduction: Anger is often accompanied by increased levels of stress. Physical activity acts as a stress reliever, as it helps reduce cortisol, the stress hormone, and induces relaxation. It provides an opportunity to clear the mind, redirect negative thoughts, and focus on the present moment.
Energy Channeling: Physical activity allows us to channel the intense energy associated with anger into something productive. Engaging in vigorous exercises, such as running, kickboxing, or weightlifting, can help release tension, frustrations, and pent-up emotions.
Enhanced Self-Control: Regular exercise contributes to improved self-control and emotional regulation. By establishing a routine that includes physical activity, we develop discipline, patience, and the ability to manage our emotions more effectively, including anger.
Improved Mental Well-being: Engaging in physical activity has been linked to a reduction in symptoms of anxiety and depression. Regular exercise promotes overall mental well-being, which can positively influence anger management.
Teaching kids responsibility contributes to effective anger management. By instilling a sense of accountability for their actions, children learn to make thoughtful choices and understand the consequences of their behavior.
Incorporating Physical Activity into Daily Life:
Here are some practical tips for integrating physical activity into your routine as a healthy coping mechanism for anger:
Choose an activity you enjoy: Find an exercise or physical activity that you genuinely enjoy and look forward to. This will increase your motivation and make it easier to stick to your routine.
Set realistic goals: Start with achievable goals and gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts. Setting small milestones will boost your confidence and keep you motivated.
Mix it up: Vary your physical activities to prevent boredom and keep yourself engaged. Explore different forms of exercise, such as yoga, swimming, dancing, or team sports, to find what suits you best.
Practice mindfulness: Combine physical activity with mindfulness techniques. Pay attention to your body and your breath while exercising, allowing yourself to be fully present in the moment. This can help calm the mind and promote a sense of inner peace.
Seek support: Consider joining group exercise classes or finding a workout buddy. Engaging in physical activity with others can provide a supportive environment and make the experience more enjoyable.
Set clear and consistent boundaries
In our fast-paced and often stressful world, managing anger has become increasingly important. Uncontrolled anger can damage relationships, hinder personal growth, and negatively impact overall well-being. One powerful tool in anger management is setting clear and consistent boundaries.
By establishing boundaries for ourselves and communicating them effectively, we can maintain healthier relationships, cultivate self-control, and foster a more peaceful and fulfilling life. In this blog post, we will delve into the significance of consistent discipline and boundaries in anger management.
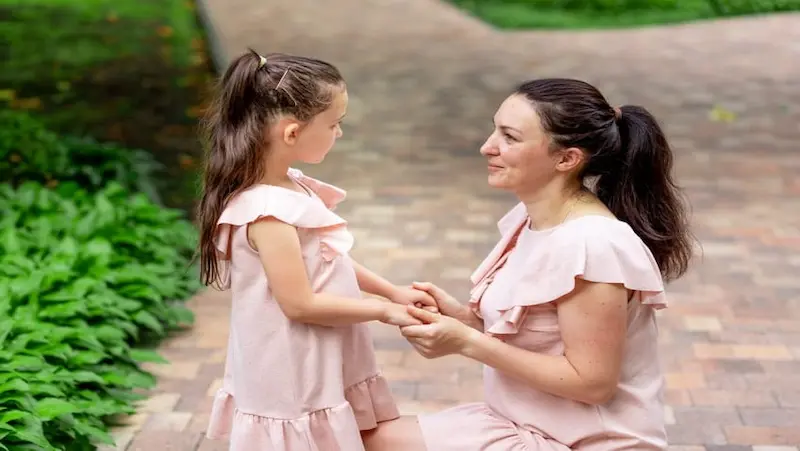

The Role of Boundaries
Boundaries act as guidelines that define acceptable behavior, both for ourselves and others. They provide structure and create a sense of safety and respect within relationships. Setting boundaries in anger management involves establishing limits for how we express and handle our anger, as well as the behavior we will tolerate from others.
Importance of Clear Boundaries
Self-Awareness: Establishing clear boundaries requires self-reflection and an understanding of our own triggers and limits. By recognizing what situations or behaviors provoke our anger, we can proactively set boundaries to prevent escalation.
Communication: Clear boundaries foster effective communication by enabling us to express our needs and expectations to others. When we communicate our boundaries calmly and assertively, we provide a framework for healthier interactions and reduce the likelihood of anger-inducing situations.
Personal Empowerment: Boundaries empower us to take charge of our emotional well-being. By clearly defining what we will and will not tolerate, we establish a foundation of self-respect and control. This, in turn, helps us navigate challenging situations with greater composure and assertiveness.
Consistency and Discipline
Setting boundaries is not a one-time task but an ongoing process that requires consistency and discipline. Without consistency, boundaries lose their effectiveness and may be easily disregarded.
Consistency demonstrates our commitment to our own well-being and sets expectations for others. Here’s why consistency and discipline are vital in anger management:
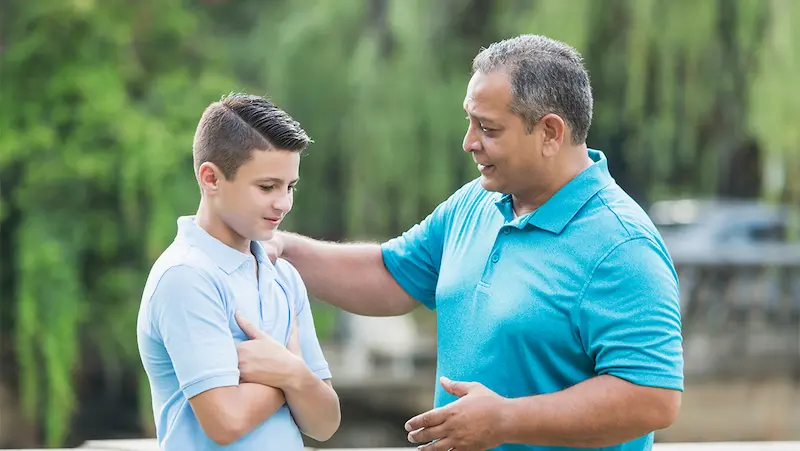

Strengthening Relationships: Consistency in upholding boundaries allows others to understand our expectations and enables them to respect our limits. This clarity in communication builds trust and fosters healthier and more respectful relationships.
Enhancing Self-Control: By adhering to our own boundaries consistently, we reinforce our self-control. This discipline helps us resist impulsive reactions and choose healthier responses to anger-inducing situations.
Modeling Behavior: Consistently practicing healthy anger management and maintaining boundaries serves as a positive example for others. Our behavior can influence those around us, encouraging them to adopt similar strategies and fostering a more harmonious environment.
Tips for Setting Clear and Consistent Boundaries
Identify Triggers: Reflect on the situations, behaviors, or actions that tend to provoke your anger. Understanding your triggers will help you set boundaries more effectively.
Define Your Limits: Clearly define what behaviors and situations you find unacceptable or intolerable. Be specific and communicate your boundaries assertively yet respectfully.
Communicate Openly: Express your boundaries calmly and assertively to those around you. Clearly communicate the consequences of crossing those boundaries, while remaining open to dialogue and negotiation when appropriate.
Practice Self-Discipline: Hold yourself accountable for maintaining your boundaries consistently. Remember that setting boundaries is an ongoing process and may require practice and adjustment.
Seek Support: Consider seeking guidance from a therapist or counselor specializing in anger management. They can provide valuable insights, strategies, and support tailored to your specific needs.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, it is imperative for parents to recognize the importance of implementing effective anger management strategies within their family dynamic. Parental anger can have a significant impact on children’s well-being, their emotional development, and the overall harmony of the household.
By acknowledging and addressing their own anger issues, parents not only prioritize their own mental health but also create a positive and nurturing environment for their children to thrive.
First and foremost, parents should strive to cultivate self-awareness and recognize the triggers that lead to their anger. Understanding the underlying causes of anger can help individuals gain better control over their emotions and prevent them from lashing out impulsively.
This self-reflection can be facilitated through various techniques, such as journaling, therapy, or seeking support from anger management programs or professionals.
In addition to communication, parents should explore and implement coping mechanisms that work best for them personally. These strategies may include deep breathing exercises, mindfulness techniques, physical activity, or engaging in hobbies that promote relaxation and stress reduction.
By developing a repertoire of healthy coping mechanisms, parents can navigate difficult situations with greater ease, reducing the likelihood of anger escalating into harmful behaviors.
In conclusion, parents play a pivotal role in shaping their children’s emotional well-being and overall development. By proactively addressing their own anger issues and implementing effective anger management strategies, parents can create a nurturing environment that promotes healthy emotional expression and fosters positive relationships within the family.
The journey toward mastering anger management is a continuous one, but the rewards of a harmonious and loving family dynamic make every effort worthwhile.
Learn more about learning money for kids and banking game for kids.
BrightChamps’ blog page offers insightful tips on time management and productive study habits, helping students excel academically. With a variety of engaging topics, it’s a valuable resource for anyone seeking educational guidance. Navigating through BrightChamps is like having a supportive study partner at your fingertips.
Frequently Asked Questions
A1. Anger management is the process of learning how to control and express anger in a healthy way. It is important for kids because it helps them develop self-control, build better relationships, and cope with challenging situations.
A2. Signs of anger management issues in children may include frequent temper tantrums, physical aggression, difficulty calming down, intense anger over small things, or trouble handling frustration.
A3. Common triggers of anger in children can include feeling misunderstood, experiencing unfairness, facing challenges or obstacles, feeling overwhelmed, or not being able to communicate their needs effectively.
A4. Teach your child to identify and express anger in healthy ways, encourage open communication, validate their feelings, teach them the appropriate vocabulary to express emotions, and model healthy anger management yourself.
A5. Effective anger management strategies for kids include deep breathing exercises, counting to ten, using calming techniques like listening to music or drawing, taking a break or walking away from the situation, and finding positive outlets for anger like physical activity.
A6. Yes, deep breathing exercises, such as belly breathing or balloon breathing, can help children manage their anger. Relaxation techniques like progressive muscle relaxation or guided imagery can also be beneficial.
A7. Help your child develop better impulse control by teaching them to recognize warning signs of anger, practicing self-calming techniques, encouraging them to think before reacting, and providing consistent discipline and boundaries.
A8. Communication plays a crucial role in teaching kids anger management skills. Encourage open dialogue, and active listening, and teach them assertive communication techniques to express their feelings and needs effectively.
A9. Create a calm and supportive environment at home by setting clear expectations, establishing consistent routines, promoting healthy coping strategies, providing emotional support, and fostering a positive and respectful atmosphere.
A10. Yes, some recommended books and resources for teaching children about anger management include “When I Feel Angry” by Cornelia Maude Spelman, “Cool Down and Work Through Anger” by Cheri J. Meiners, and websites like KidsHealth.org or APA.org with articles on child anger management.


 We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.
We are an army of educators and passionate learners from BrightChamps family, committed to providing free learning resources to kids, parents & students.